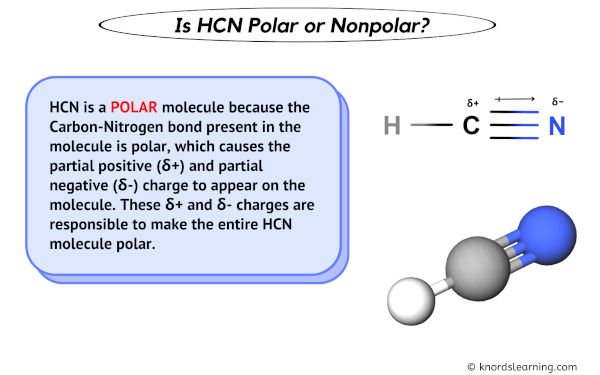
HCN is a POLAR molecule.
But why?
And how can you say that HCN is a polar molecule?
Want to know the reason?
Let’s dive into it!
HCN is a POLAR molecule because the Carbon-Nitrogen bond present in the molecule is polar, which causes the partial positive (ẟ+) and partial negative (ẟ-) charge to appear on the molecule. These ẟ+ and ẟ- charges are responsible to make the entire HCN molecule polar.
Let me explain this in detail with the help of HCN lewis structure and its 3D geometry.
Why is HCN a Polar molecule? (Explained in 2 Steps)
HCN is a polar molecule because it has poles of partial positive charge (ẟ+) and partial negative charge (ẟ-) on it.
Let me explain this to you in 2 steps!
Step #1: Draw the lewis structure
Here is a skeleton of HCN lewis structure and it contains one Carbon-Hydrogen bond and one Carbon-Nitrogen bond.

(Note: If you want to know the steps of drawing the HCN lewis dot structure, then visit this article: HCN lewis structure, Or you can also watch this short 2 minute video).
So from the above diagram we have come to know that the HCN molecule has one Carbon-Hydrogen bond and one Carbon-Nitrogen bond.
Now in the next step we have to check whether the Carbon-Hydrogen bond and Carbon-Nitrogen bond are polar or nonpolar.
And we also have to check the molecular geometry of HCN.
Step #2: Check the bond polarity and molecular geometry
The chemical bonds can be either nonpolar, polar or ionic depending on the difference of the electronegativity values (ΔEN) between the two atoms.
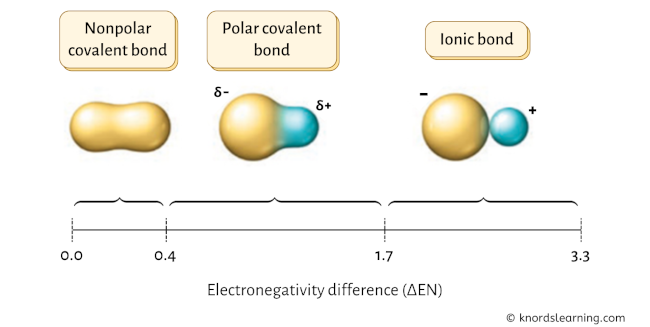
Have a look at the above image.
- If the electronegativity difference (ΔEN) is less than 0.4, then the bond is nonpolar covalent bond.
- If the electronegativity difference (ΔEN) is between 0.4 to 1.7, then the bond is polar covalent bond.
- If the electronegativity difference (ΔEN) is greater than 1.7, then the bond is an ionic bond. [1] [2] [3] [4]
Now let’s come to the example of HCN molecule. It has one Carbon-Hydrogen bond and one Carbon-Nitrogen bond.
You can see the electronegativity values of Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Nitrogen (N) atoms from the periodic table given below.
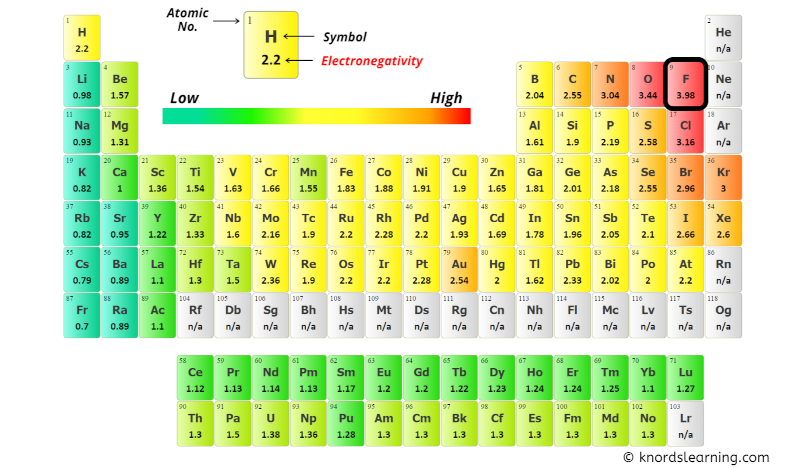
From the above image;
- Electronegativity of Carbon (C) = 2.55 [5]
- Electronegativity of Hydrogen (H) = 2.2 [6]
- Electronegativity of Nitrogen (N) = 3.04 [7]
Now let’s see the polarity of each bond.
For C-H bond;
The electronegativity difference (ΔEN) = 2.55 – 2.2 = 0.35
This value is less than 0.4, which indicates that the bond between Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) is nonpolar.
Hence, each C-H bond is a nonpolar covalent bond.
For Carbon-Nitrogen bond;
The electronegativity difference (ΔEN) = 3.04 – 2.55 = 0.49
This value lies between 0.4 to 1.7, which indicates that the bond between Carbon (C) and Nitrogen (N) is polar.
Hence, the Carbon-Nitrogen bond is a polar covalent bond.

You can see in the above image that because of large electronegativity difference of Carbon and Nitrogen atom, the partial positive charge (ẟ+) appears on the Carbon atom (C) and partial negative charge (ẟ-) appears on the Nitrogen atom (N).
From this, you can easily get the idea that the HCN molecule is a polar molecule.
But let’s also see its 3D molecular geometry for better understanding.
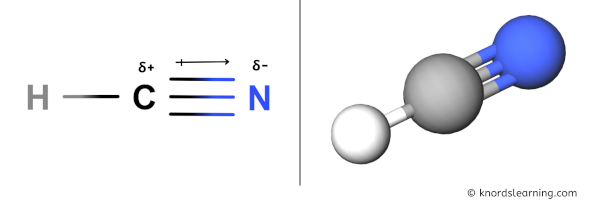
Have a look at this 3D structure of HCN. The more electronegative nitrogen atom (N) has a tendency to pull the shared electron pair towards itself, which results in partial positive charge on carbon atom (C) and partial negative charge on nitrogen atom (N).
Because of this, there are positive and negative poles of charges on the overall molecule of HCN.
Hence, the HCN molecule is a polar molecule.
I hope you have understood the reason behind the polar nature of HCN molecule.
See the polarity of other molecules to make your concepts clear:
Is CH2O Polar or Nonpolar?
Is XeF4 Polar or Nonpolar?
Is SF6 Polar or Nonpolar?
Is BCl3 Polar or Nonpolar?
Is CHCl3 Polar or Nonpolar?
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.