The Charge of NH3 (Ammonia) is 0.
But the question is how can you say that the charge on NH3 (Ammonia) is 0?
Well you can say this by calculating its formal charge.
So let’s calculate the formal charge of NH3 (Ammonia).
You can also refer to the below video from which you will learn to find charge of any ion.
Calculating the formal charge of NH3 using lewis structure
In order to calculate the formal charge on NH3 (Ammonia), you should know the Lewis dot structure of NH3 (Ammonia).
Here is the lewis structure of NH3.
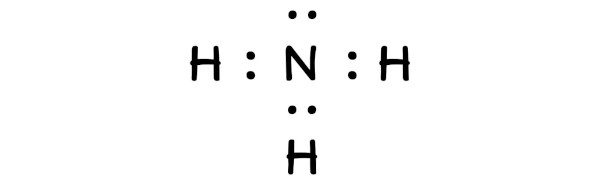
Now using the above lewis structure of NH3, you have to find the formal charge on each atom that is present in the NH3 molecule.
For calculating the formal charge, you need to remember this formula;
Formal charge = Valence electrons – Nonbonding electrons – (Bonding electrons)/2
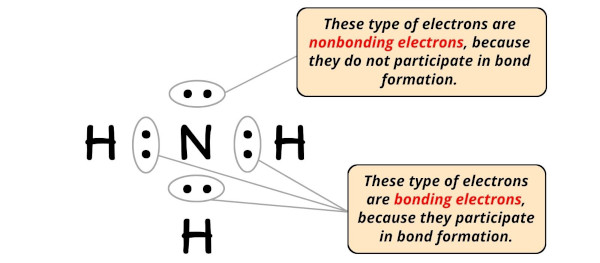
You can see the bonding and nonbonding electrons of NH3 from the image given below.
So now let’s calculate the formal charge on each individual atom present in NH3.
Formal charge on Nitrogen atom:
Valence electrons = 5 (as it is in group 15 on periodic table) [1]
Nonbonding electrons = 2
Bonding electrons = 6
So according to the formula of formal charge, you will get;
Formal charge on Nitrogen = Valence electrons – Nonbonding electrons – (Bonding electrons)/2 = 5 – 2 – (6/2) = 0
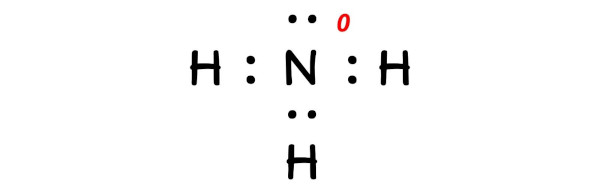
So the formal charge on nitrogen atom is 0.
Formal charge on Hydrogen atom:
Valence electron = 1 (as it is in group 1 on periodic table) [2]
Nonbonding electrons = 0
Bonding electrons = 2
So according to the formula of formal charge, you will get;
Formal charge on Hydrogen = Valence electrons – Nonbonding electrons – (Bonding electrons)/2 = 1 – 0 – (2/2) = 0
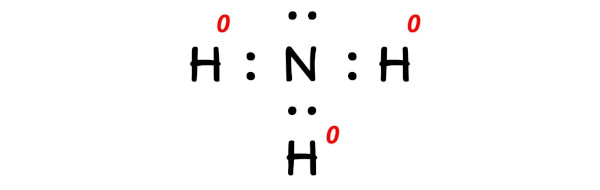
So the formal charge on hydrogen atom is 0.
Now you can see that all the atoms of NH3 have 0 formal charge.
This indicates that the overall NH3 (Ammonia) molecule also has 0 charge and hence it is a neutral molecule.
I hope you have understood the above calculations for the formal charge of NH3 (Ammonia).
Check out some other related topics for your practice.
Related topics:
Charge of Bromine (Br)
Charge of OH (Hydroxide ion)
Charge of Oxygen (O)
Charge of Lead (Pb)
Charge of Potassium (K)
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.