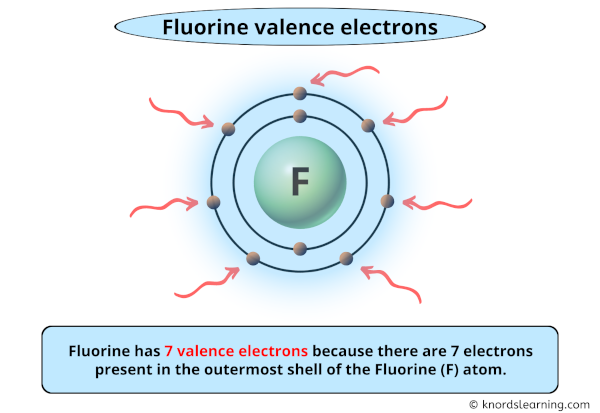
So you have seen the above image by now, right?
Awesome! You can see that fluorine has 7 valence electrons.
But how can you say that Fluorine has 7 valence electrons
+
How can you find these valence electrons?
Let’s discuss this in short.
Fluorine has 7 valence electrons because there are 7 electrons present in the outermost shell of the Fluorine (F) atom.
Now let’s see how you can easily find the valence electrons of Fluorine atom (F).
If you don’t want to read the texts, then you can also watch this video.
How to find the Valence Electrons? (2 Methods)
In order to find the valence electrons of Fluorine atom (F), you can use two methods.
Method 1: From the Periodic Table
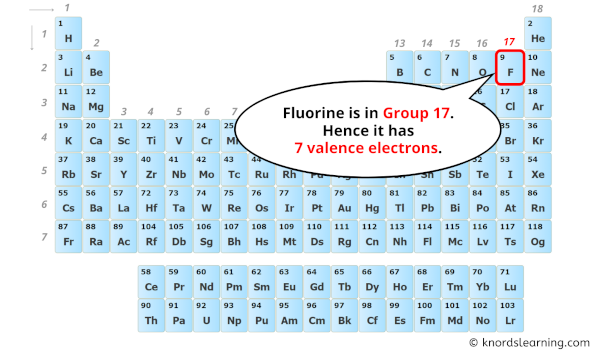
To find out the valence electrons of Fluorine, you have to see the position of fluorine in the periodic table.
More specifically, you have to see the group wise position of Fluorine element in the periodic table.
From the above image, you can see that the Fluorine (F) is present in the group 17 of periodic table.
(Note: Group 17 is also called group 7A).
So, as the fluorine element is present in group 17, it has 7 valence electrons.
In this way, by knowing the position of fluorine element in periodic table, you can easily find its valence electrons.
Now let’s see another method for finding the number of valence electrons in fluorine.
Method 2: From the Electron Configuration
If you want to find the valence electrons of fluorine from its electron configuration, then you should know its electron configuration first.
Now there are many methods to write the electron configurations, but here I will show you the easiest method, i.e by using Aufbau principle.
Aufbau principle: The Aufbau principle simply states that the orbitals with the lower energy are filled first and then the orbitals with higher energy levels are filled.
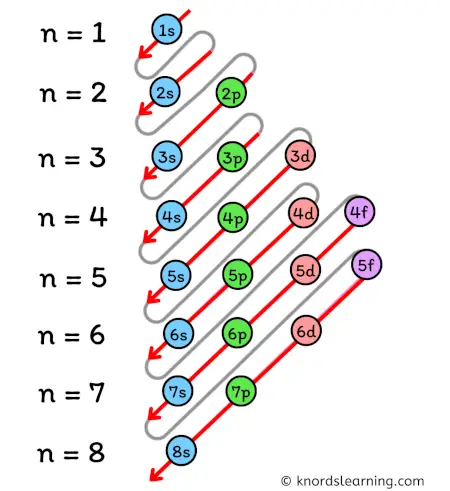
According to the Aufbau principle, the orbitals are filled in the following order:
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p, and so on.
Also the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in s, p, d & f orbitals are mentioned in the below table.
| Orbitals | Maximum capacity of electrons [1] |
| s | 2 |
| p | 6 |
| d | 10 |
| f | 14 |
Now let’s try to find the electron configuration of Fluorine by using the Aufbau principle.
Electron Configuration of Fluorine:
Follow the steps mentioned below to get the electron configuration of Fluorine.
- To write the electron configuration of fluorine, we should first know the total number of electrons present in a fluorine atom.
- The fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons because its atomic number is 9 and it is a neutral atom. [2]
- Now we have to fill these 9 electrons in the atomic orbitals according to the Aufbau principle.
- According to the Aufbau principle, the electrons will be filled first in 1s orbital, then in 2s orbital, then in 2p orbital, and so on…
- So from the Aufbau principle, we can get the electron configuration of the fluorine atom as 1s2 2s2 2p5. [3]
Now in this electron configuration of fluorine, we have to see the total number of electrons present in the highest energy level.
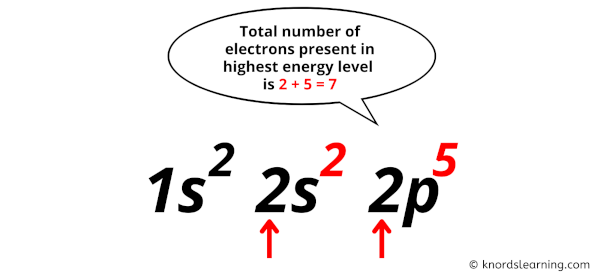
You can see in the electron configuration of fluorine (1s2 2s2 2p5) that the highest energy level is 2. And the total number of electrons present in this energy level is 2 + 5 = 7.
So by knowing the electron configuration, we have found that the Fluorine has 7 valence electrons.
I hope you have understood the methods of finding the valence electrons in fluorine.
See more related topics for your practice;
Neon Valence Electrons
Aluminum Valence Electrons
Silicon Valence Electrons
Phosphorus Valence Electrons
Sulfur Valence Electrons
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.