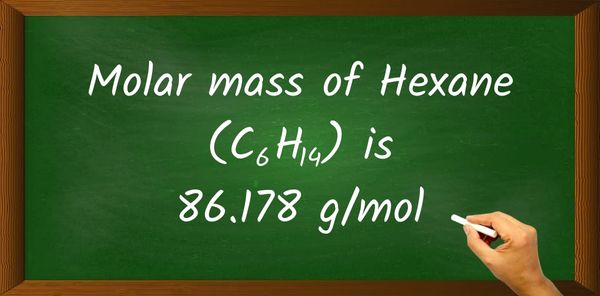
Molar mass of Hexane (C6H14) is 86.178 g/mol.
Well, now you have come to know the molar mass of Hexane.
But how can you get this value?
Let me show you the calculation to get the molar mass of Hexane (C6H14).
If you are a visual learner like me, then here is a short one minute video for you.
Hexane (C6H14) Molar Mass Calculation
If you have a periodic table with you, then you can easily calculate the molar mass of Hexane (C6H14).
Because the molar mass of any molecule (or compound) can be calculated by simply adding the molar masses of individual atoms.
Now here we have to find the molar mass of Hexane (C6H14).
So for that, have a look at the periodic table given below.
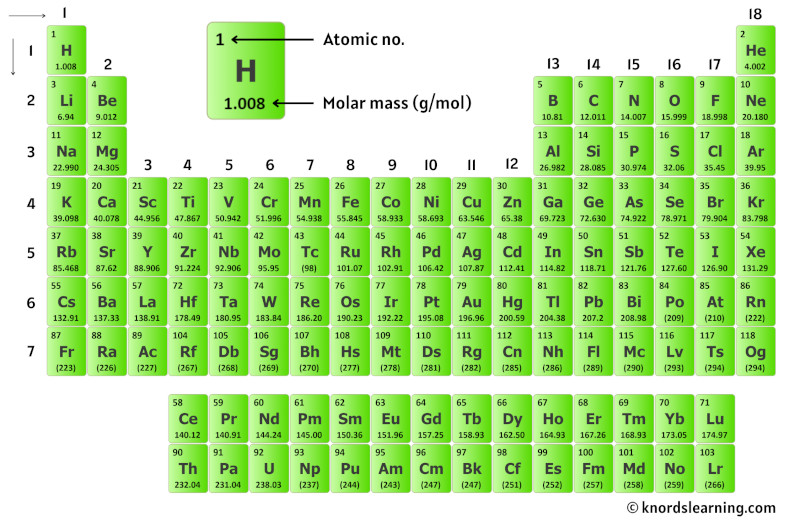
You can see the molar mass value of all the atoms from this periodic table.
Now in Hexane (C6H14), there are 6 Carbon atoms and 14 Hydrogen atoms.
So let’s look at the molar mass of Carbon and Hydrogen from the above periodic table.
You can see that;
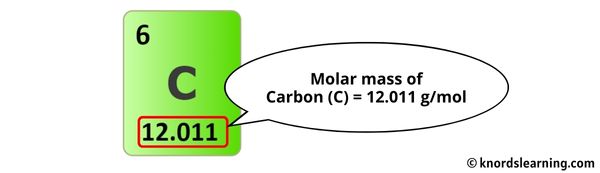
The molar mass of Carbon is 12.011 g/mol. [1]
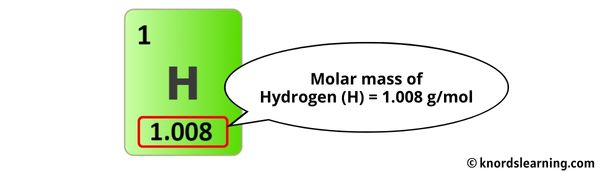
The molar mass of Hydrogen is 1.008 g/mol. [2]
Now, to calculate the molar mass of Hexane, you just have to add the molar mass of all the individual atoms that are present in Hexane.
You can see that in Hexane, there are 6 Carbon atoms and 14 Hydrogen atoms.
So, Molar mass of Hexane (C6H14) = Molar mass of 6 Carbon (C) atoms + Molar mass of 14 Hydrogen (H) atoms.
= (12.011) 6 + (1.008) 14
= 72.066 + 14.112
= 86.178 g/mol
Hence the Molar mass of Hexane is 86.178 g/mol.
I hope you have understood the short and simple calculation for finding the molar mass of Hexane.
Remember
- In some books, you may see the unit of molar mass as grams/mole or g/mole. But all these units (i.e g/mol, grams/mole and g/mole) are the same.
- Always follow the calculation order to avoid any mistakes in calculation. First solve the brackets, then multiplications and at last do the final addition.
- And don’t forget to put the unit g/mol to your final calculated molar mass.
Check out other related topics for more practice;
HBr (Hydrobromic acid) Molar Mass
Aspirin (C9H8O4) Molar Mass
Butane (C4H10) Molar Mass
KNO3 (Potassium nitrate) Molar Mass
C3H8 (Propane) Molar Mass
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.