What is a Bohr model?
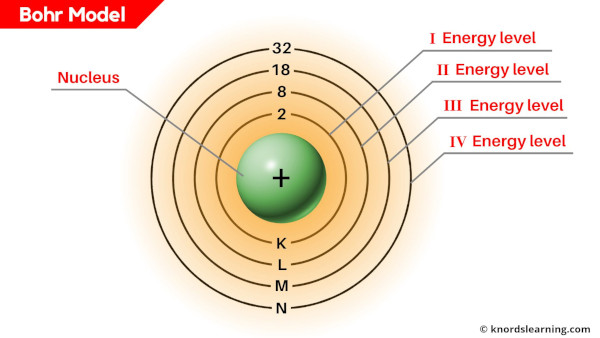
Bohr model is a structural model in which the negatively charged electrons revolve around the positively charged nucleus. This is similar to the planets revolving around the sun, except that the orbits are non-planar.
The electrons move in a fixed orbits (shells) and each orbit has a fixed energy.
Each orbit (or shell) can hold a certain number of electrons.
Here is a simple table showing the number of electrons that can be accommodated in each shell.
Number of electrons in each shell;
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
|---|---|
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 32 |
| . | . |
| . | . |
Thus, 1st shell can hold 2 electrons, 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons, 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons, 4th shell can hold 32 electrons, and so on. [1]
Bohr Model of All Elements
Bohr diagrams of all elements are shown in the table below.
| Atomic no. | Elements | Bohr model of Elements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bohr model of Hydrogen (H) |
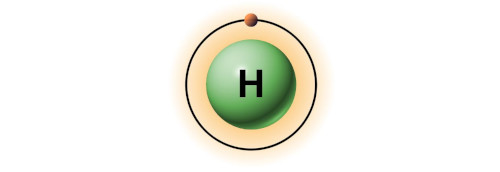 1 |
| 2 | Bohr model of Helium (He) |
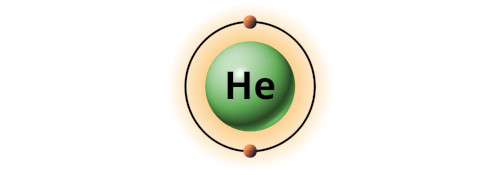 2 |
| 3 | Bohr model of Lithium (Li) |
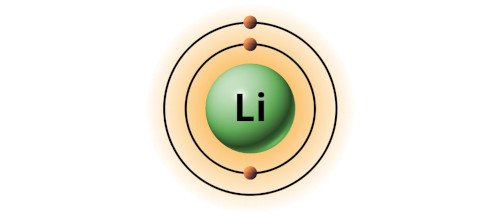 2, 1 |
| 4 | Bohr model of Beryllium (Be) |
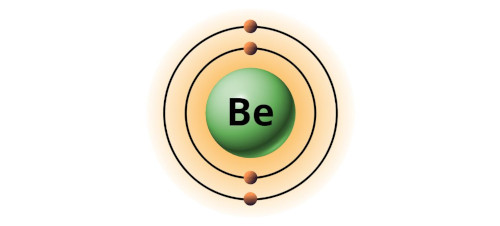 2, 2 |
| 5 | Bohr model of Boron (B) | 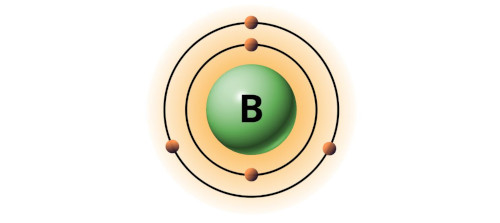 2, 3 2, 3 |
| 6 | Bohr model of Carbon (C) | 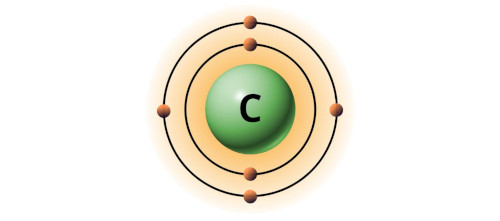 2, 4 2, 4 |
| 7 | Bohr model of Nitrogen (N) |
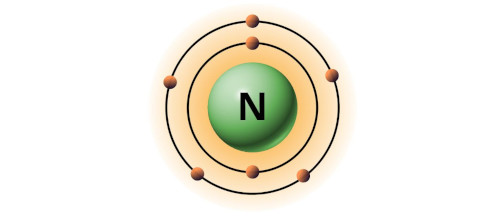 2, 5 |
| 8 | Bohr model of Oxygen (O) |
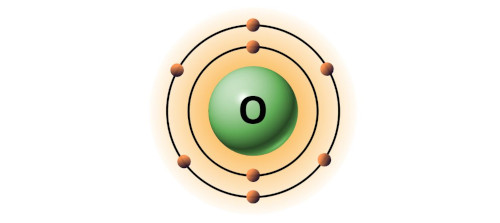 2, 6 |
| 9 | Bohr model of Fluorine (F) |
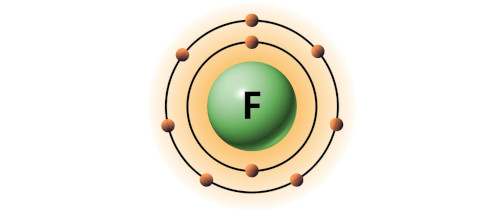 2, 7 |
| 10 | Bohr model of Neon (Ne) |
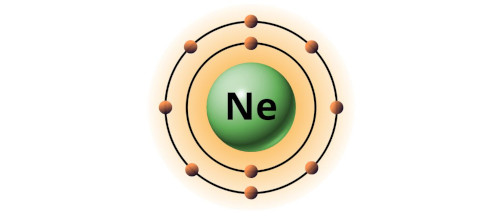 2, 8 |
| 11 | Bohr model of Sodium (Na) |
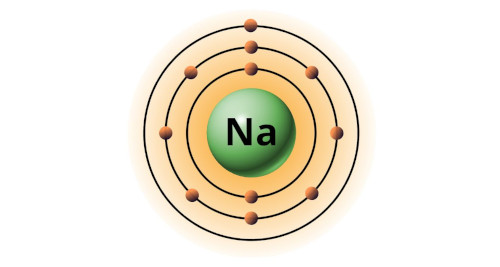 2, 8, 1 |
| 12 | Bohr model of Magnesium (Mg) |
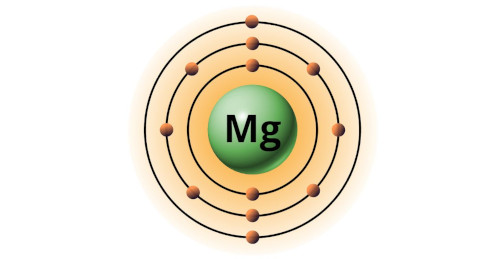 2, 8, 2 |
| 13 | Bohr model of Aluminum (Al) |
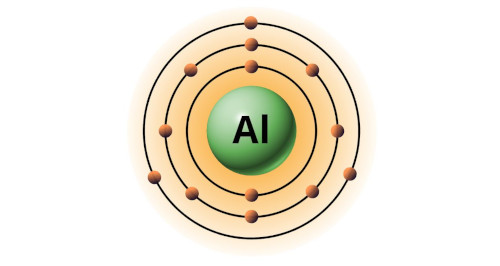 2, 8, 3 |
| 14 | Bohr model of Silicon (Si) |
2, 8, 4 |
| 15 | Bohr model of Phosphorus (P) |
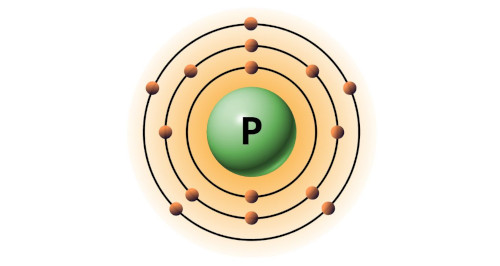 2, 8, 5 |
| 16 | Bohr model of Sulfur (S) |
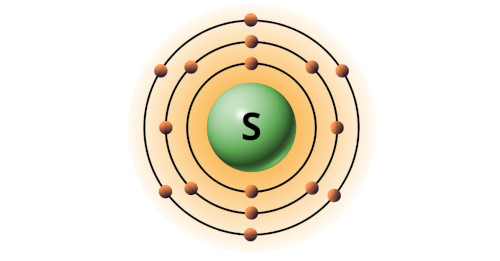 2, 8, 6 |
| 17 | Bohr model of Chlorine (Cl) |
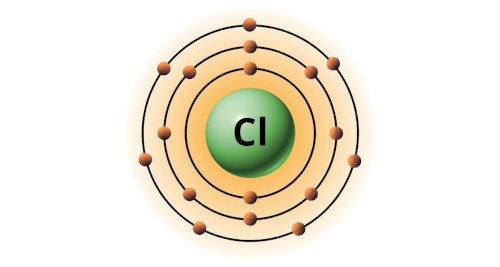 2, 8, 7 |
| 18 | Bohr model of Argon (Ar) |
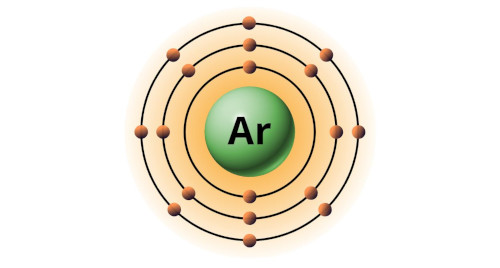 2, 8, 8 |
| 19 | Bohr model of Potassium (K) |
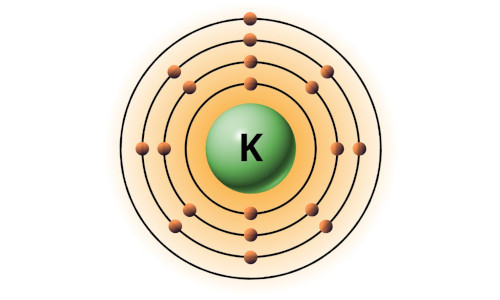 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| 20 | Bohr model of Calcium (Ca) |
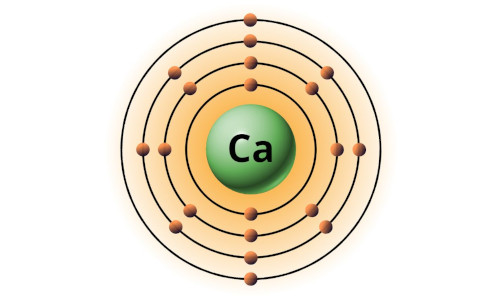 2, 8, 8, 2 |
| 21 | Bohr model of Scandium (Sc) |
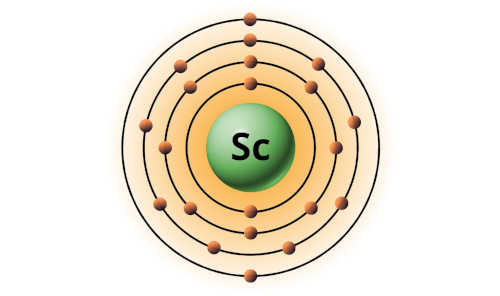 2, 8, 9, 2 |
| 22 | Bohr model of Titanium (Ti) |
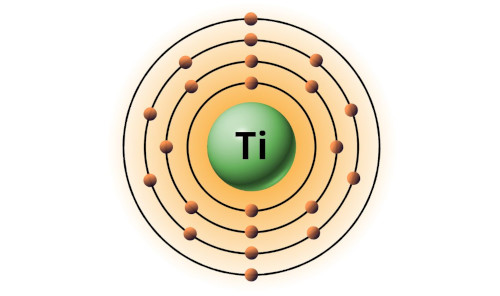 2, 8, 10, 2 |
| 23 | Bohr model of Vanadium (V) |
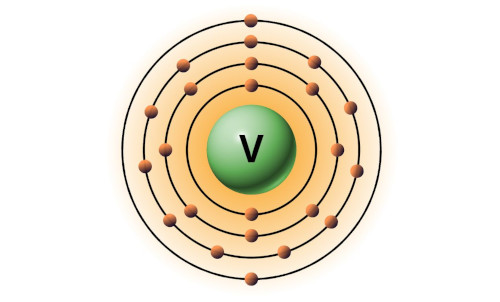 2, 8, 11, 2 |
| 24 | Bohr model of Chromium (Cr) |
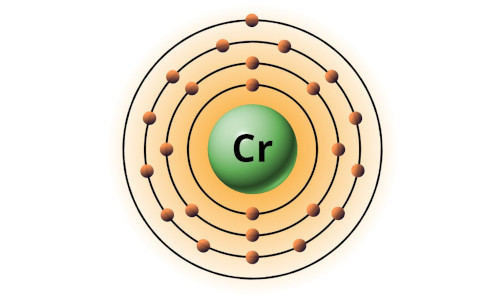 2, 8, 13, 1 |
| 25 | Bohr model of Manganese (Mn) |
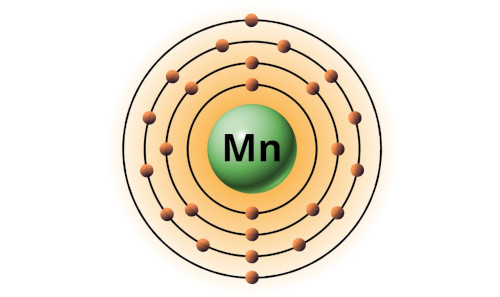 2, 8, 13, 2 |
| 26 | Bohr model of Iron (Fe) |
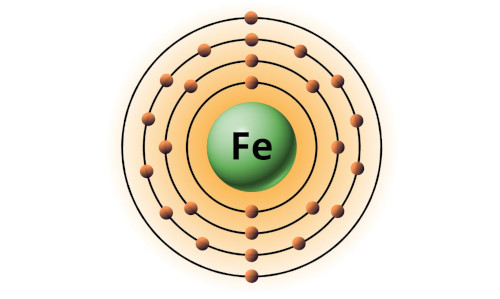 2, 8, 14, 2 |
| 27 | Bohr model of Cobalt (Co) |
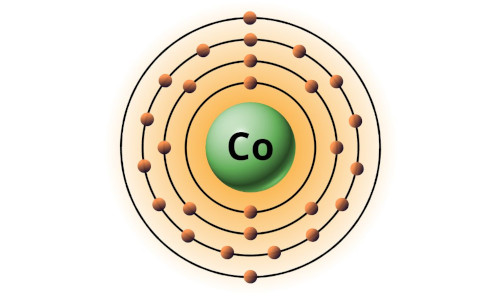 2, 8, 15, 2 |
| 28 | Bohr model of Nickel (Ni) |
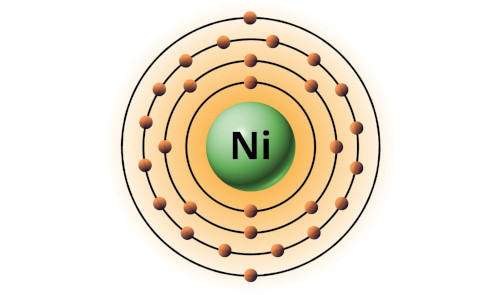 2, 8, 16, 2 |
| 29 | Bohr model of Copper (Cu) |
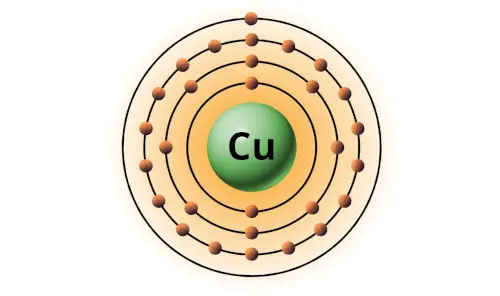 2, 8, 18, 1 |
| 30 | Bohr model of Zinc (Zn) |
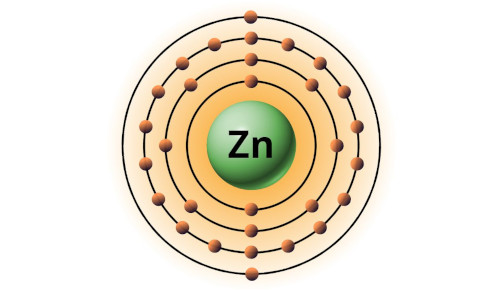 2, 8, 18, 2 |
| 31 | Bohr model of Gallium (Ga) |
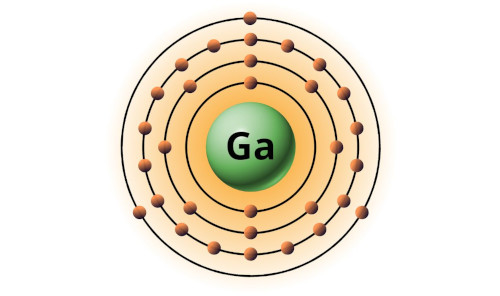 2, 8, 18, 3 |
| 32 | Bohr model of Germanium (Ge) |
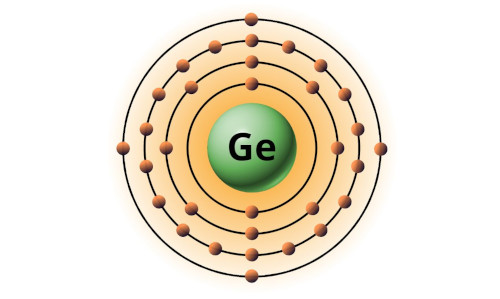 2, 8, 18, 4 |
| 33 | Bohr model of Arsenic (As) |
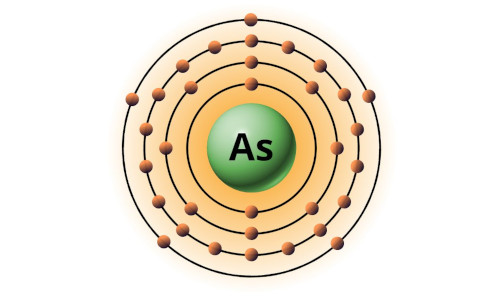 2, 8, 18, 5 |
| 34 | Bohr model of Selenium (Se) |
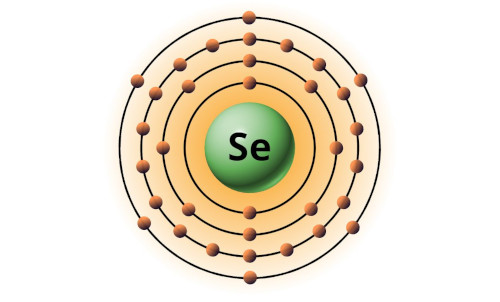 2, 8, 18, 6 |
| 35 | Bohr model of Bromine (Br) |
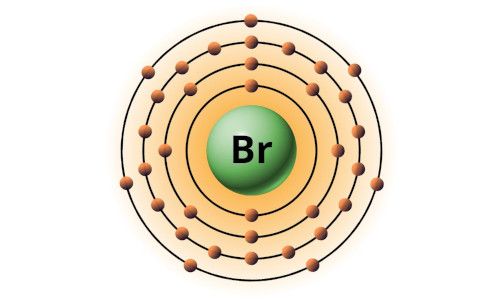 2, 8, 18, 7 |
| 36 | Bohr model of Krypton (Kr) |
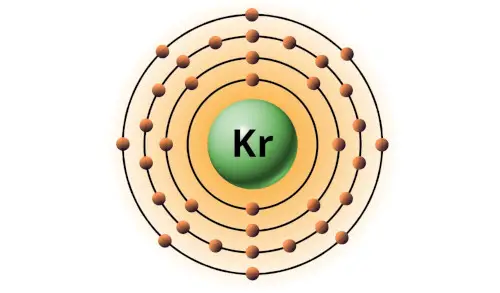 2, 8, 18, 8 |
| 37 | Bohr model of Rubidium (Rb) |
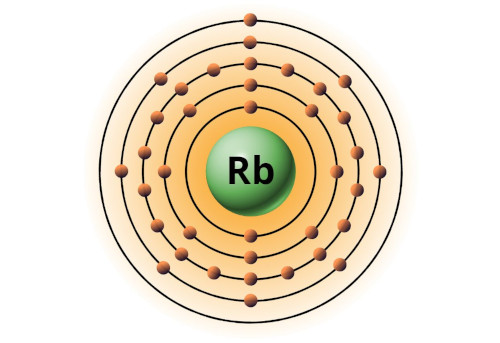 2, 8, 18, 8, 1 |
| 38 | Bohr model of Strontium (Sr) |
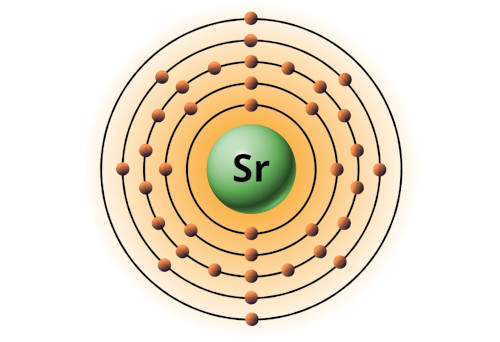 2, 8, 18, 8, 2 |
| 39 | Bohr model of Yttrium (Y) |
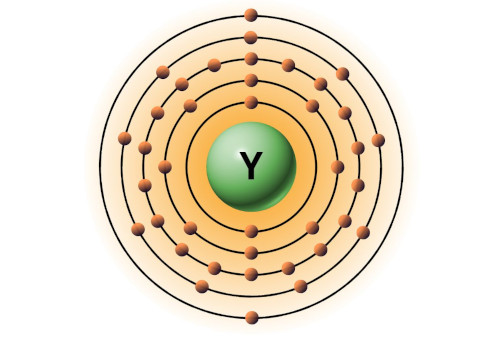 2, 8, 18, 9, 2 |
| 40 | Bohr model of Zirconium (Zr) |
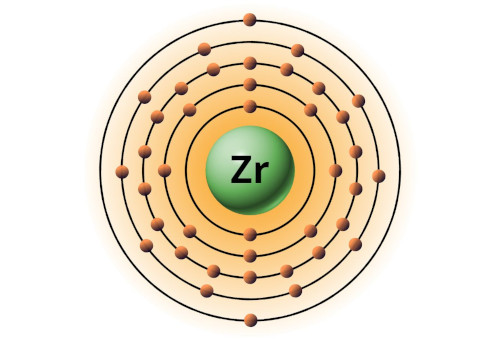 2, 8, 18, 10, 2 |
| 41 | Bohr model of Niobium (Nb) |
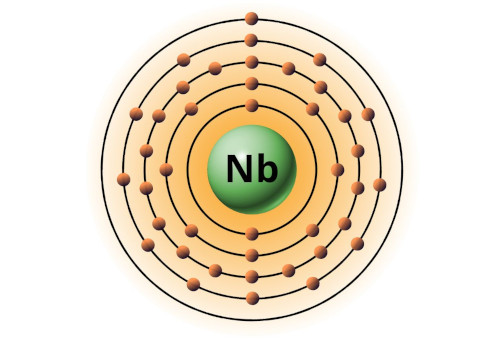 2, 8, 18, 12, 1 |
| 42 | Bohr model of Molybdenum (Mo) |
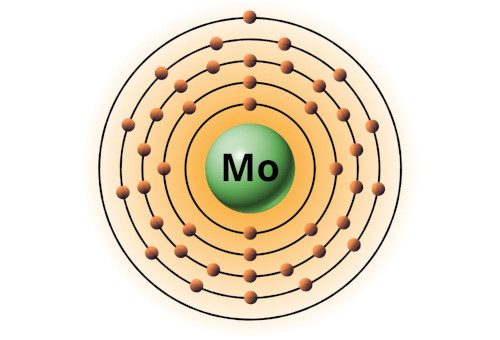 2, 8, 18, 13, 1 |
| 43 | Bohr model of Technetium (Tc) |
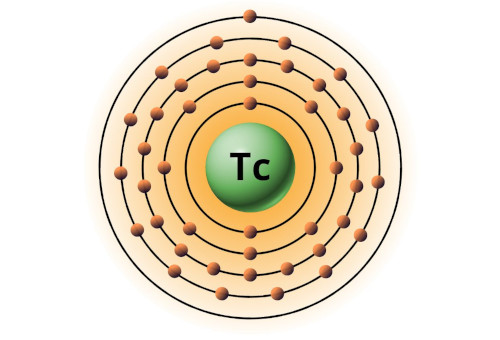 2, 8, 18, 14, 1 |
| 44 | Bohr model of Ruthenium (Ru) |
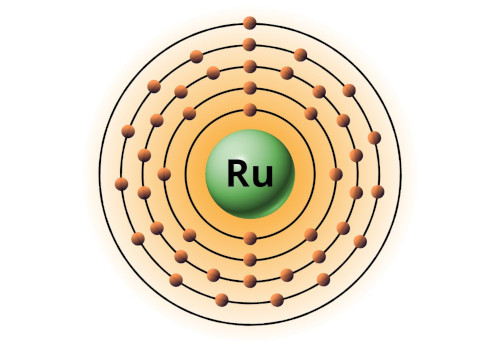 2, 8, 18, 15, 1 |
| 45 | Bohr model of Rhodium (Rh) |
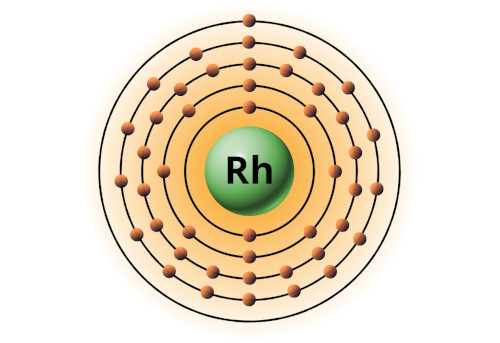 2, 8, 18, 16, 1 |
| 46 | Bohr model of Palladium (Pd) |
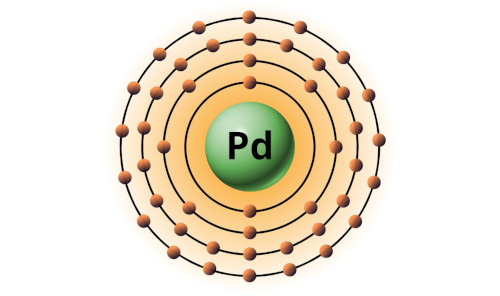 2, 8, 18, 18 |
| 47 | Bohr model of Silver (Ag) |
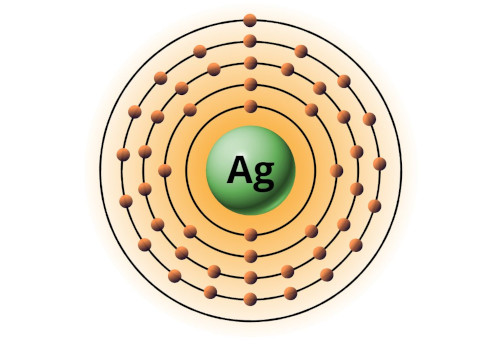 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 |
| 48 | Bohr model of Cadmium (Cd) |
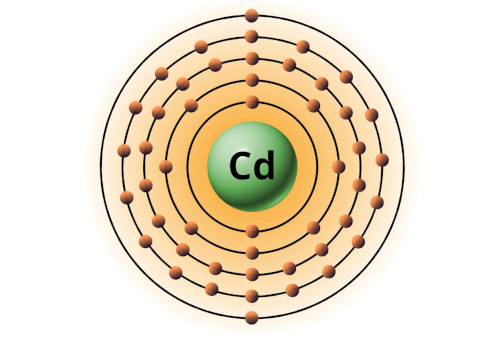 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 |
| 49 | Bohr model of Indium (In) |
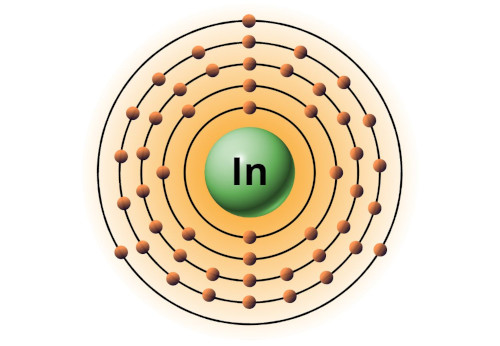 2, 8, 18, 18, 3 |
| 50 | Bohr model of Tin (Sn) |
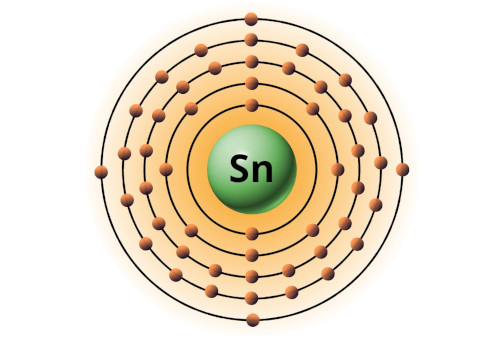 2, 8, 18, 18, 4 |
| 51 | Bohr model of Antimony (Sb) |
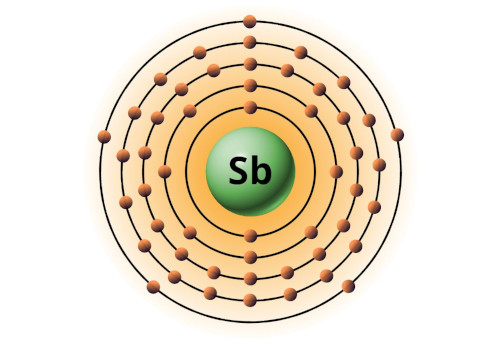 2, 8, 18, 18, 5 |
| 52 | Bohr model of Tellurium (Te) |
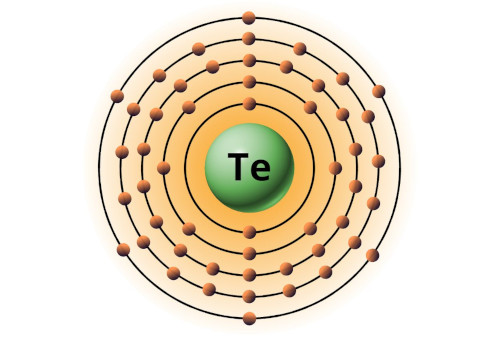 2, 8, 18, 18, 6 |
| 53 | Bohr model of Iodine (I) |
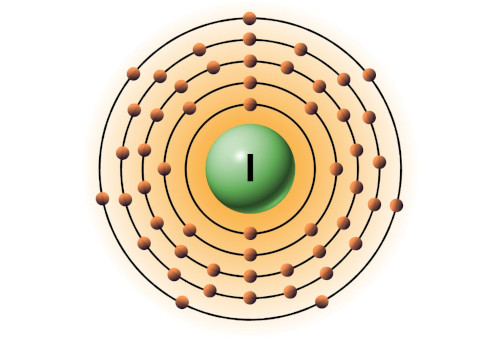 2, 8, 18, 18, 7 |
| 54 | Bohr model of Xenon (Xe) |
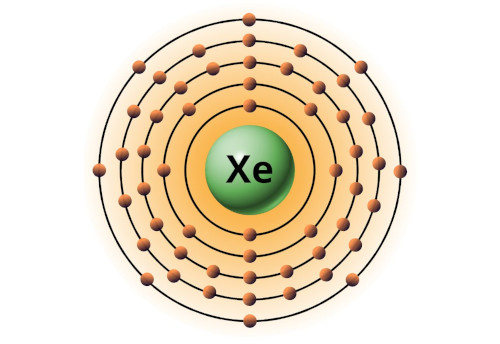 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 |
| 55 | Bohr model of Caesium (Cs) |
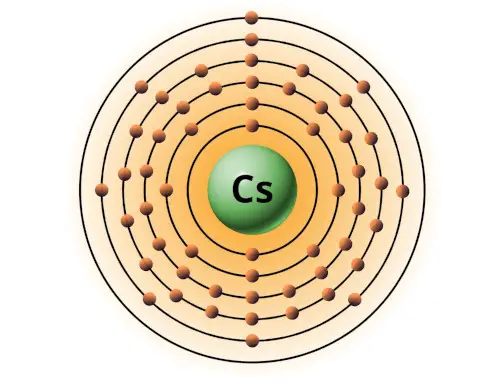 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1 |
| 56 | Bohr model of Barium (Ba) |
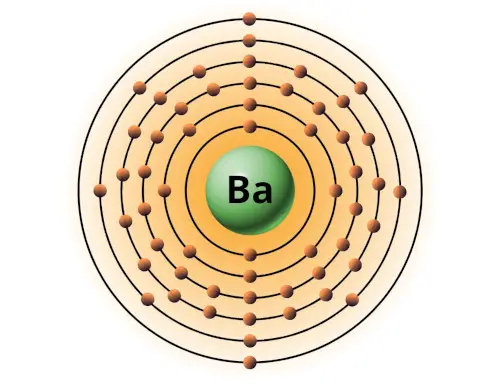 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2 |
| 57 | Bohr model of Lanthanum (La) |
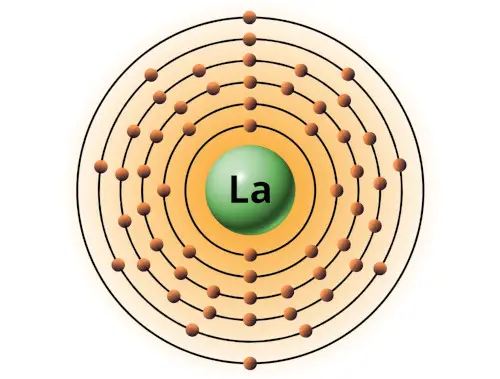 2, 8, 18, 18, 9, 2 |
| 58 | Bohr model of Cerium (Ce) |
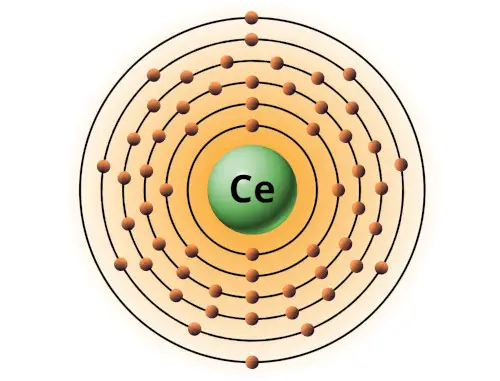 2, 8, 18, 19, 9, 2 |
| 59 | Bohr model of Praseodymium (Pr) |
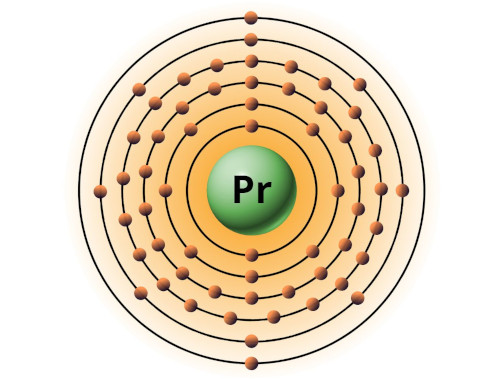 2, 8, 18, 21, 8, 2 |
| 60 | Bohr model of Neodymium (Nd) |
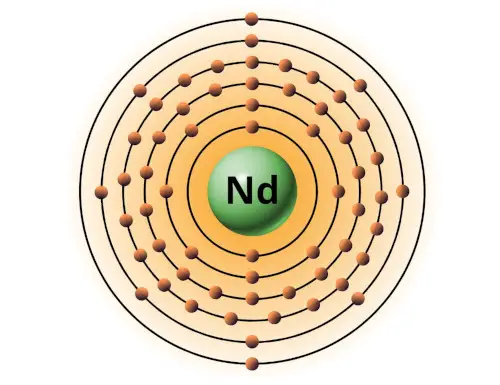 2, 8, 18, 22, 8, 2 |
| 61 | Bohr model of Promethium (Pm) |
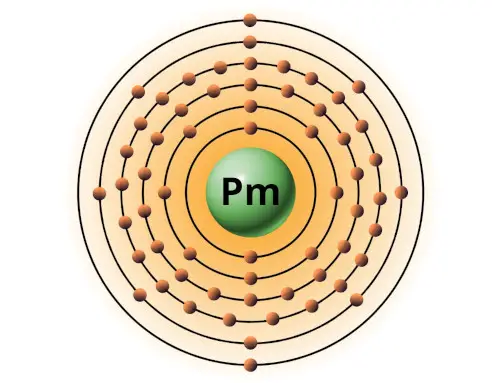 2, 8, 18, 23, 8, 2 |
| 62 | Bohr model of Samarium (Sm) |
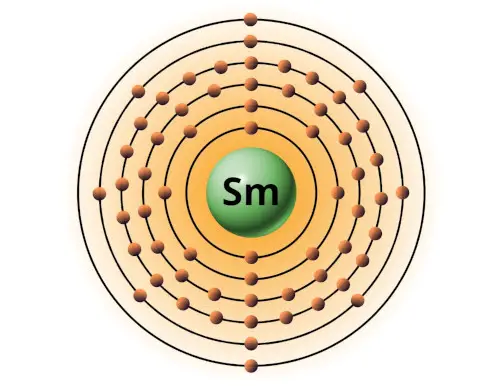 2, 8, 18, 24, 8, 2 |
| 63 | Bohr model of Europium (Eu) |
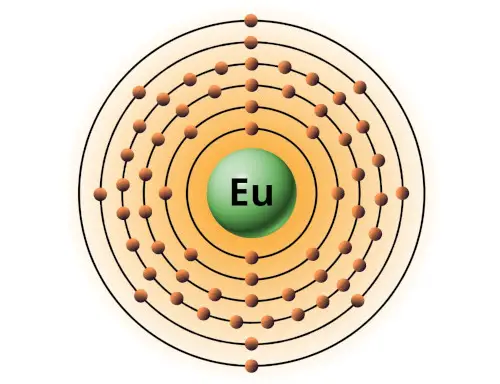 2, 8, 18, 25, 8, 2 |
| 64 | Bohr model of Gadolinium (Gd) |
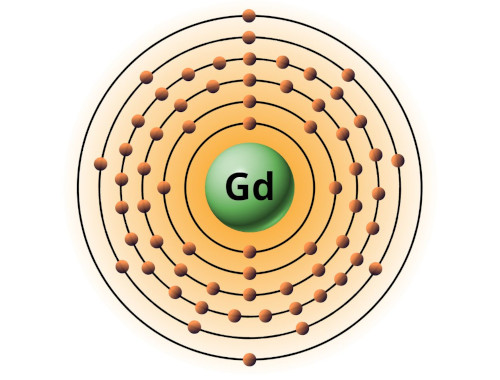 2, 8, 18, 25, 9, 2 |
| 65 | Bohr model of Terbium (Tb) |
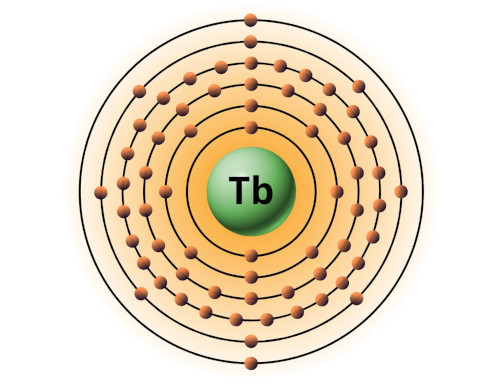 2, 8, 18, 27, 8, 2 |
| 66 | Bohr model of Dysprosium (Dy) |
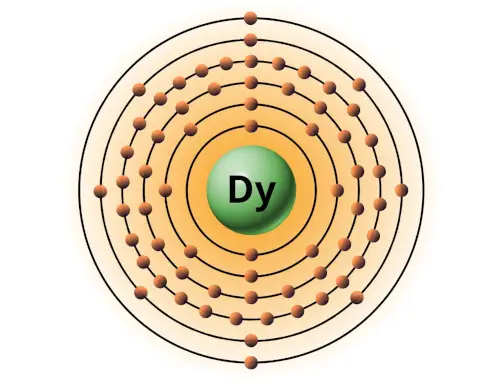 2, 8, 18, 28, 8, 2 |
| 67 | Bohr model of Holmium (Ho) |
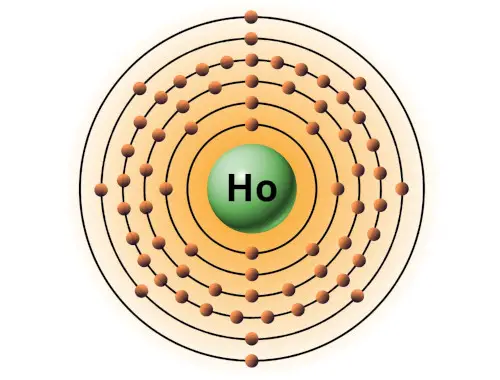 2, 8, 18, 29, 8, 2 |
| 68 | Bohr model of Erbium (Er) |
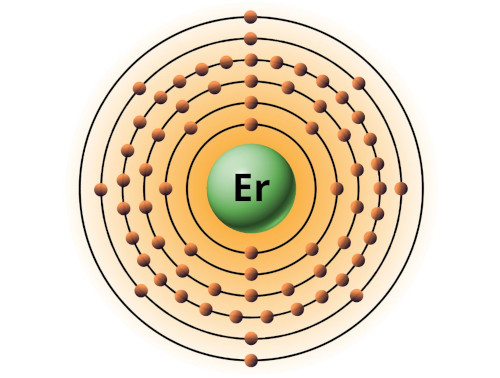 2, 8, 18, 30, 8, 2 |
| 69 | Bohr model of Thulium (Tm) |
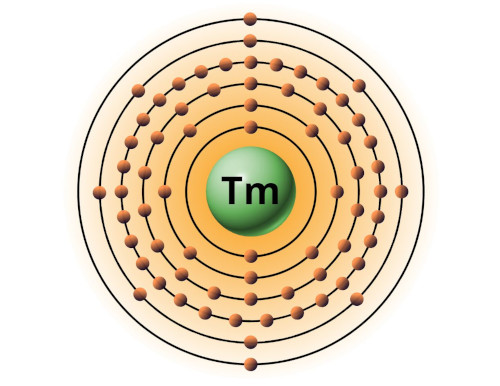 2, 8, 18, 31, 8, 2 |
| 70 | Bohr model of Ytterbium (Yb) |
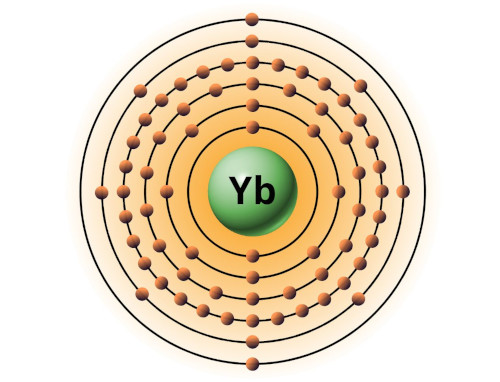 2, 8, 18, 32, 8, 2 |
| 71 | Bohr model of Lutetium (Lu) |
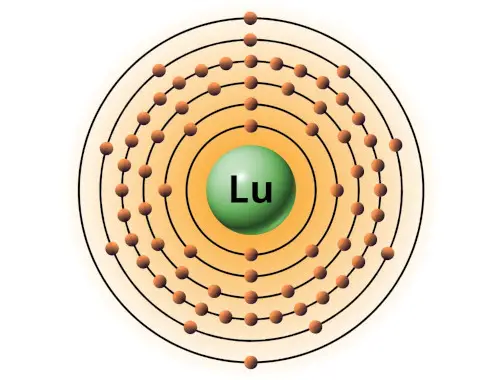 2, 8, 18, 32, 9, 2 |
| 72 | Bohr model of Hafnium (Hf) |
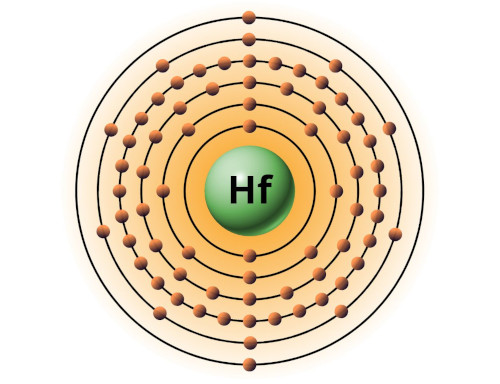 2, 8, 18, 32, 10, 2 |
| 73 | Bohr model of Tantalum (Ta) |
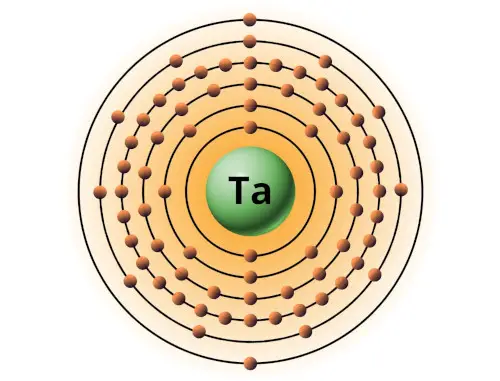 2, 8, 18, 32, 11, 2 |
| 74 | Bohr model of Tungsten (W) |
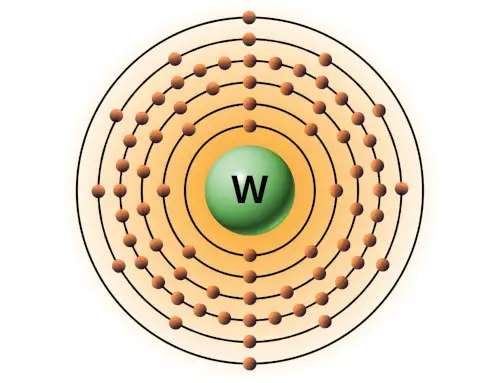 2, 8, 18, 32, 12, 2 |
| 75 | Bohr model of Rhenium (Re) |
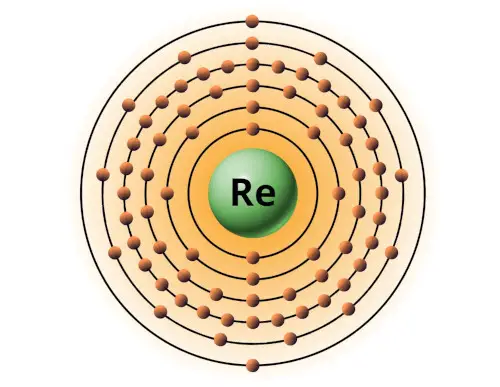 2, 8, 18, 32, 13, 2 |
| 76 | Bohr model of Osmium (Os) |
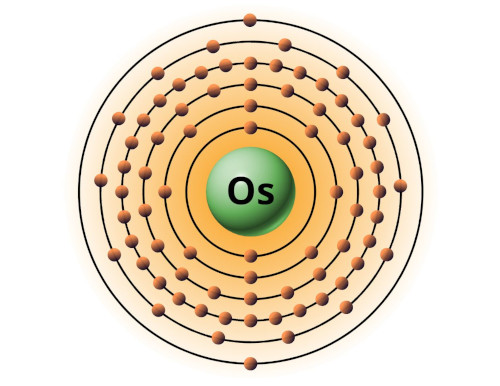 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2 |
| 77 | Bohr model of Iridium (Ir) |
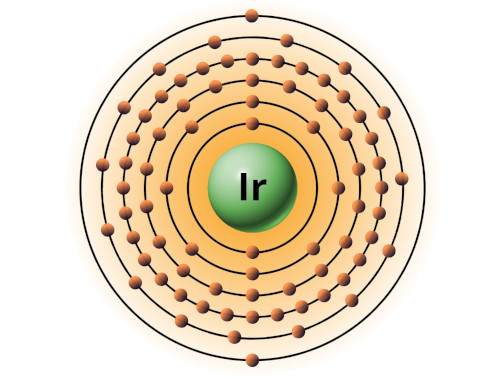 2, 8, 18, 32, 15, 2 |
| 78 | Bohr model of Platinum (Pt) |
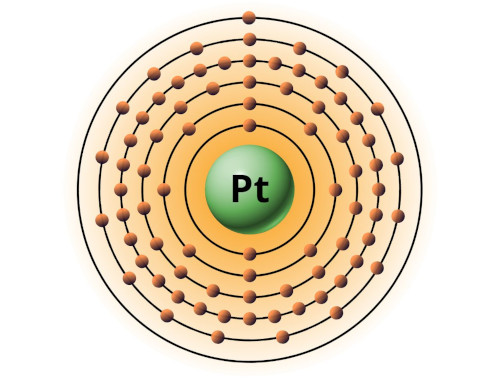 2, 8, 18, 32, 17, 1 |
| 79 | Bohr model of Gold (Au) |
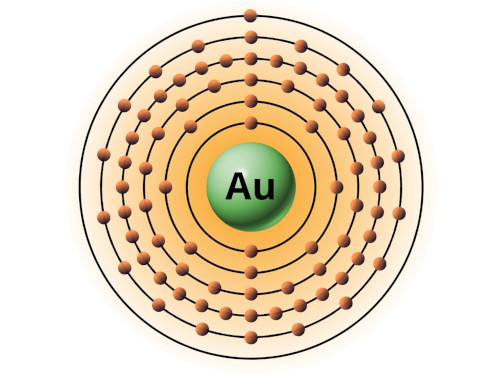 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 1 |
| 80 | Bohr model of Mercury (Hg) |
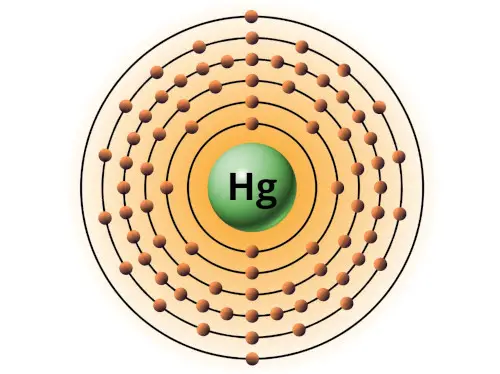 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 2 |
| 81 | Bohr model of Thallium (Tl) |
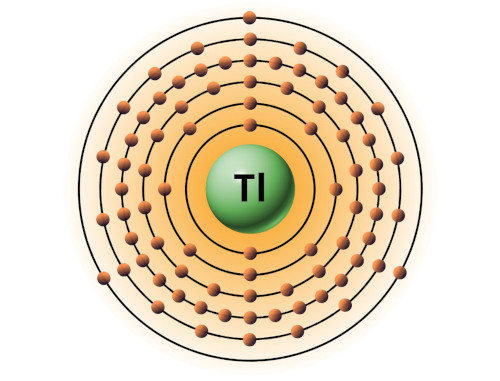 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 3 |
| 82 | Bohr model of Lead (Pb) |
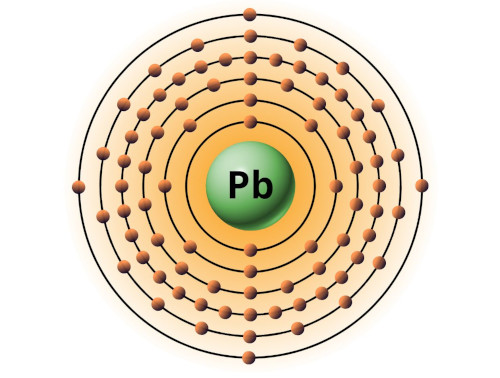 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 4 |
| 83 | Bohr model of Bismuth (Bi) |
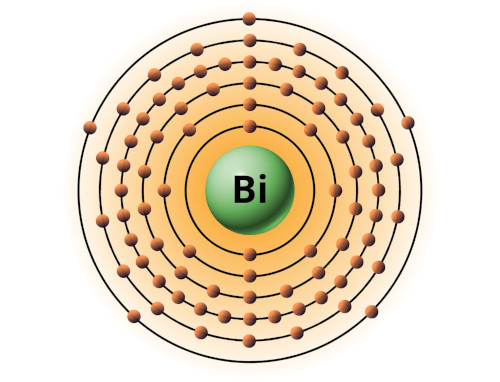 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5 |
| 84 | Bohr model of Polonium (Po) |
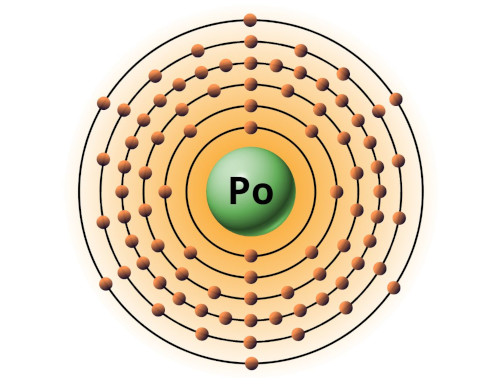 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 6 |
| 85 | Bohr model of Astatine (At) |
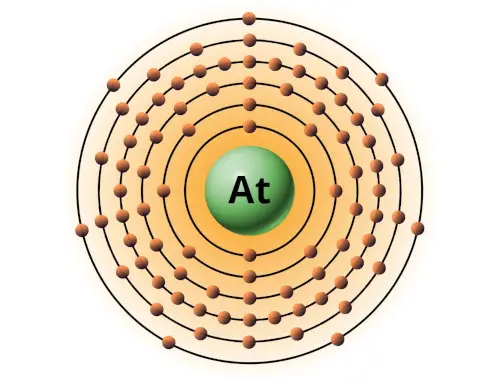 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 7 |
| 86 | Bohr model of Radon (Rn) |
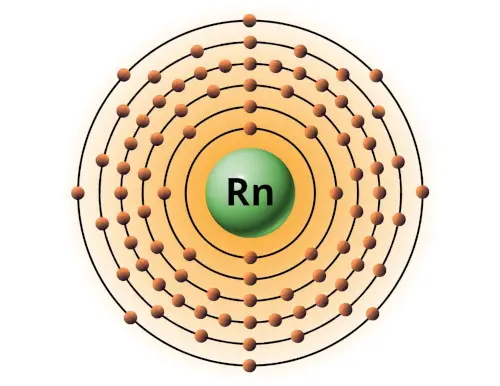 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8 |
| 87 | Bohr model of Francium (Fr) |
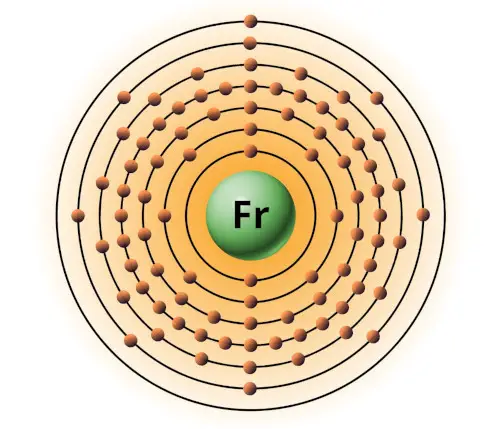 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 1 |
| 88 | Bohr model of Radium (Ra) |
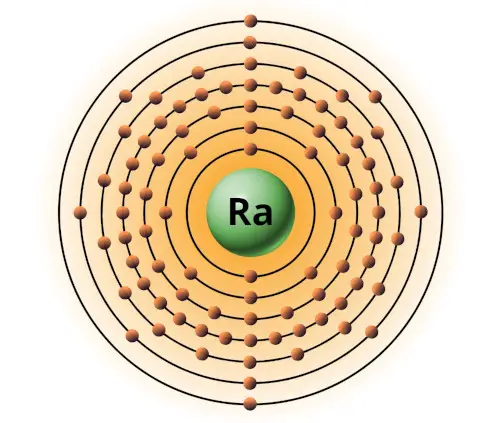 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 2 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 2
|
| 89 | Bohr model of Actinium (Ac) |
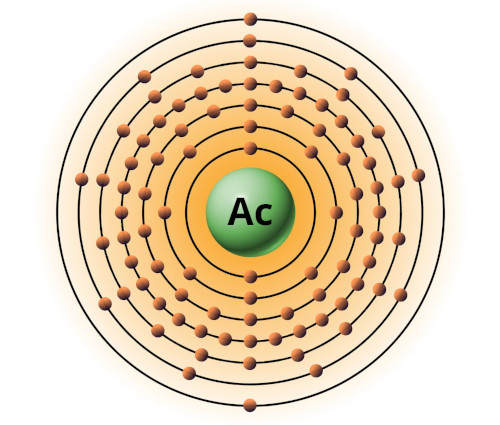 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2 |
| 90 | Bohr model of Thorium (Th) |
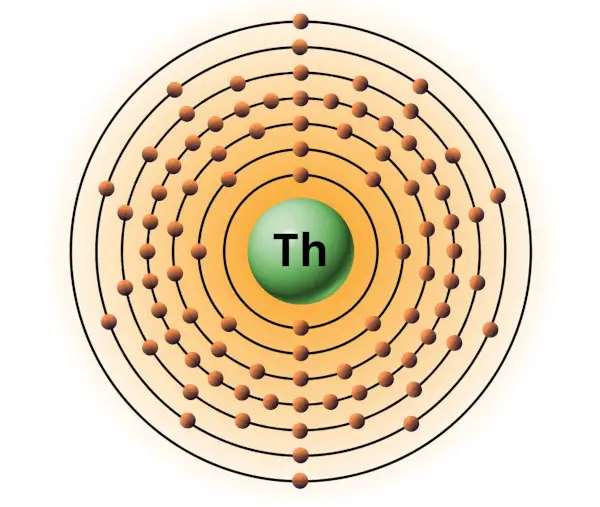 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 10, 2 |
| 91 | Bohr model of Protactinium (Pa) |
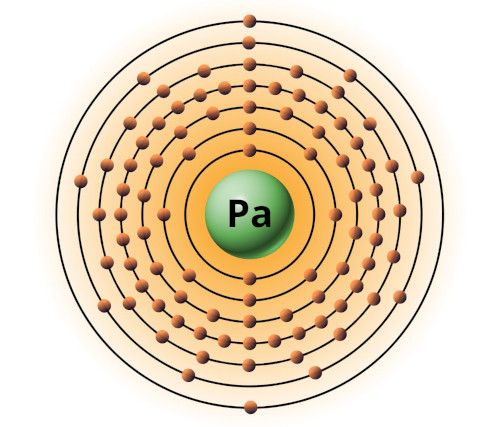 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2 |
| 92 | Bohr model of Uranium (U) |
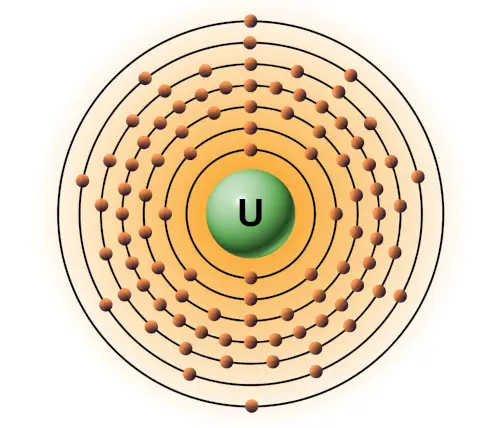 2, 8, 18, 32, 21, 9, 2 |
| 93 | Bohr model of Neptunium (Np) |
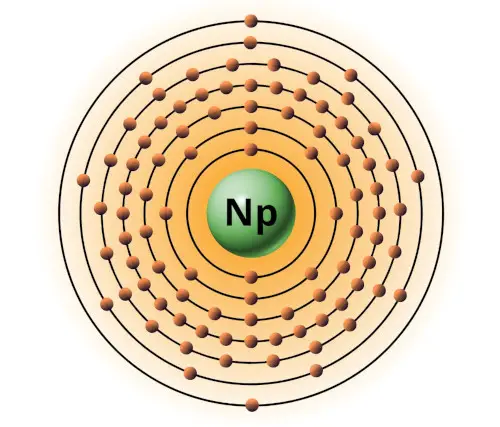 2, 8, 18, 32, 22, 9, 2 |
| 94 | Bohr model of Plutonium (Pu) |
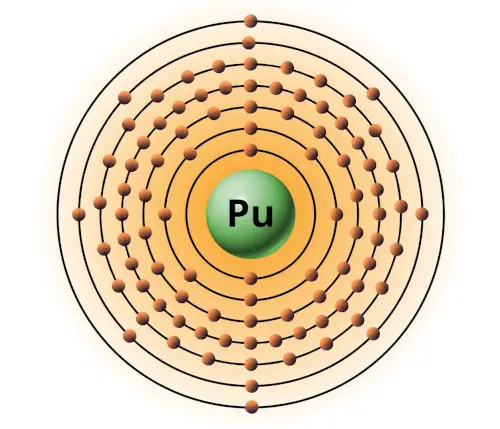 2, 8, 18, 32, 24, 8, 2 |
| 95 | Bohr model of Americium (Am) |
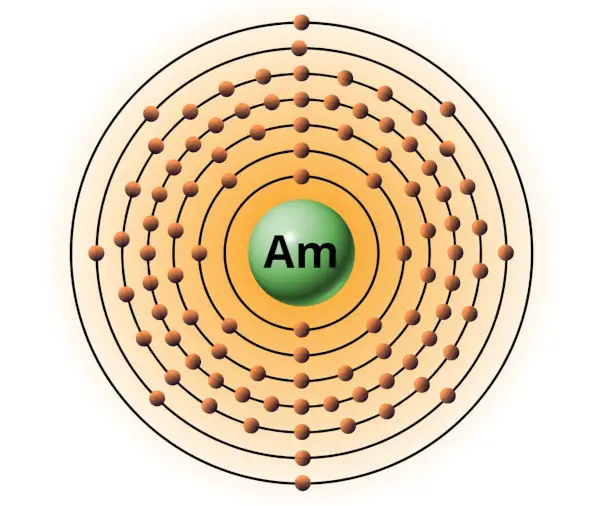 2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 8, 2 |
| 96 | Bohr model of Curium (Cm) |
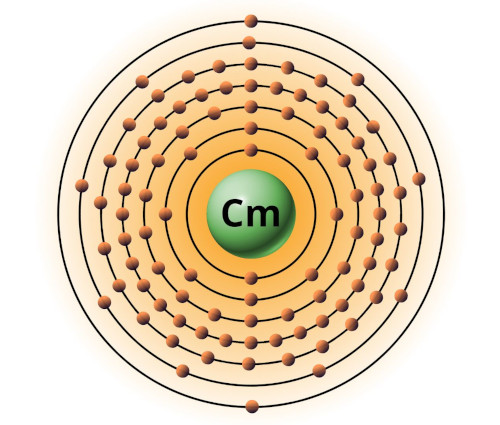 2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 9, 2 |
| 97 | Bohr model of Berkelium (Bk) |
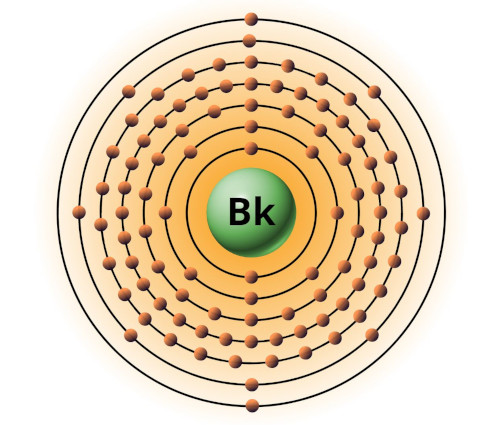 2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2 |
| 98 | Bohr model of Californium (Cf) |
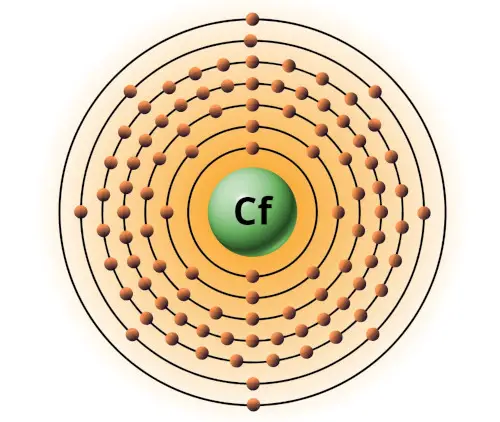 2, 8, 18, 32, 28, 8, 2 |
| 99 | Bohr model of Einsteinium (Es) |
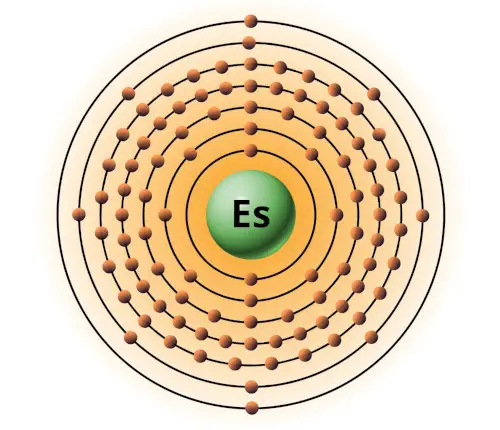 2, 8, 18, 32, 29, 8, 2 |
| 100 | Bohr model of Fermium (Fm) |
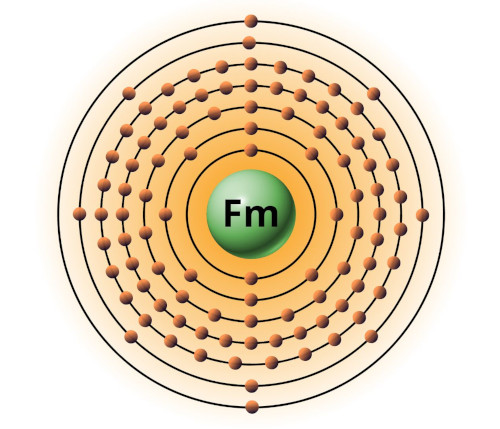 2, 8, 18, 32, 30, 8, 2 |
| 101 | Bohr model of Mendelevium (Md) |
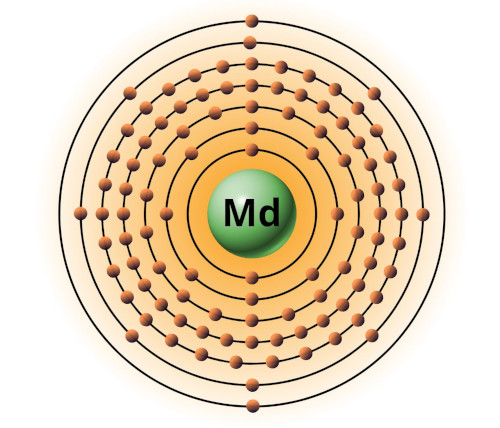 2, 8, 18, 32, 31, 8, 2 |
| 102 | Bohr model of Nobelium (No) |
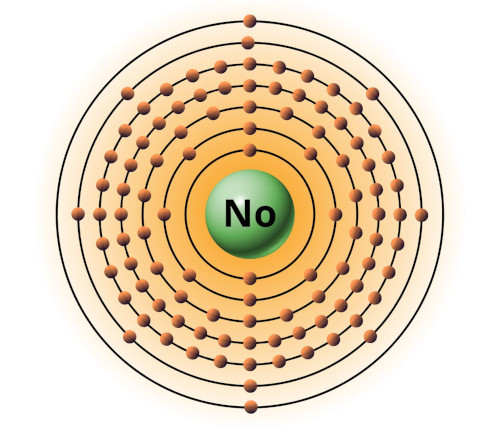 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 2 |
| 103 | Bohr model of Lawrencium (Lr) |
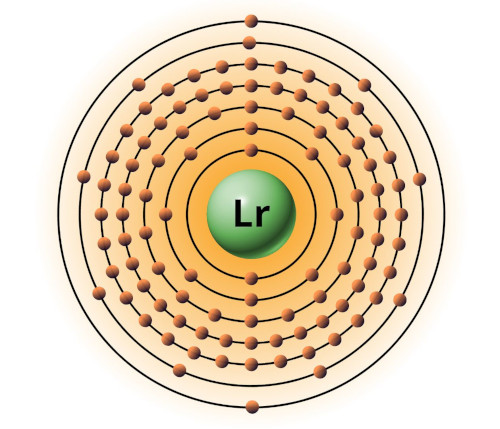 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 9, 2 |
| 104 | Bohr model of Rutherfordium (Rf) |
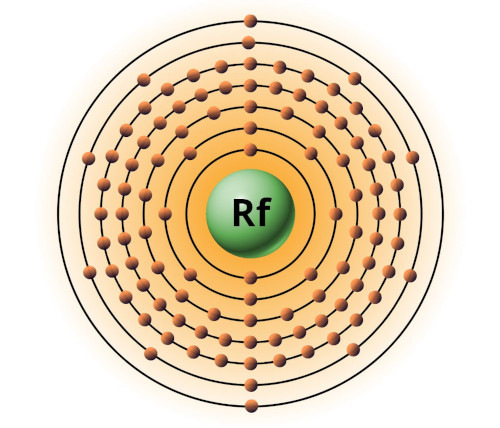 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 10, 2 |
| 105 | Bohr model of Dubnium (Db) |
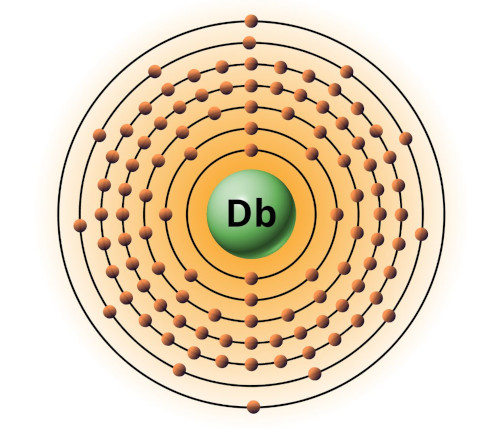 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 11, 2 |
| 106 | Bohr model of Seaborgium (Sg) |
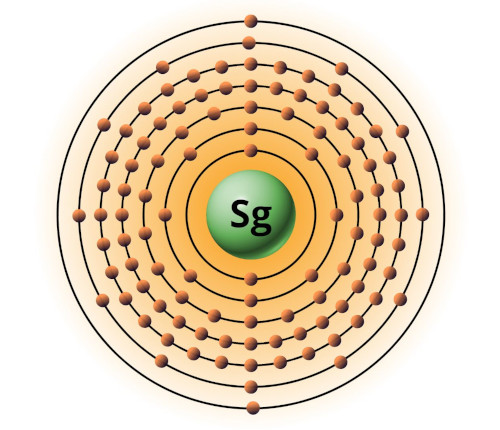 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 12, 2 |
| 107 | Bohr model of Bohrium (Bh) |
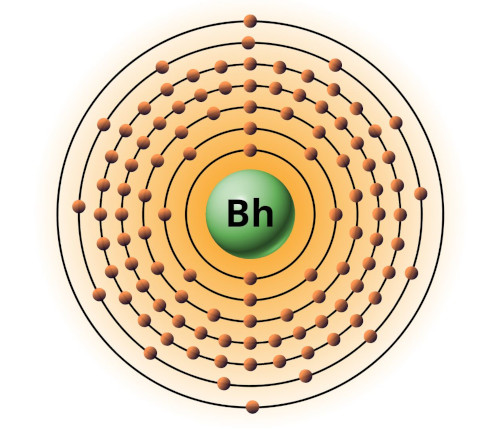 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 12, 2 |
| 108 | Bohr model of Hassium (Hs) |
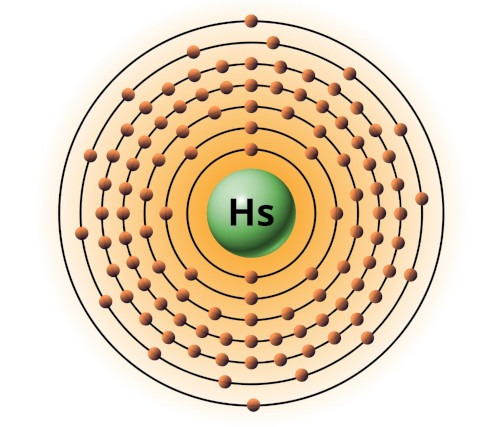 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 14, 2 |
| 109 | Bohr model of Meitnerium (Mt) |
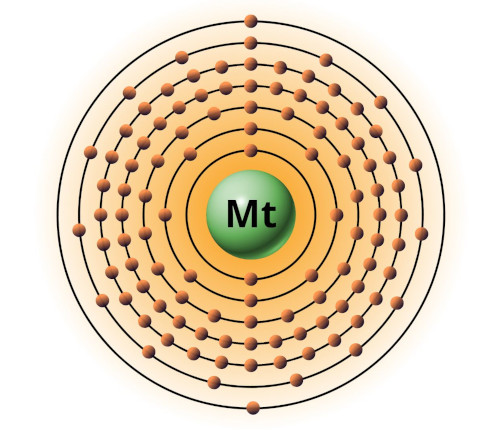 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 15, 2 |
| 110 | Bohr model of Darmstadtium (Ds) |
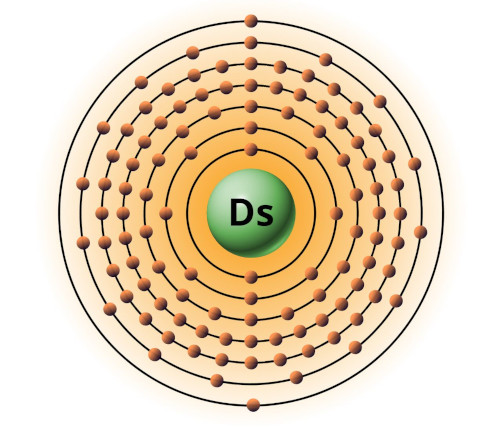 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 16, 2 |
| 111 | Bohr model of Roentgenium (Rg) |
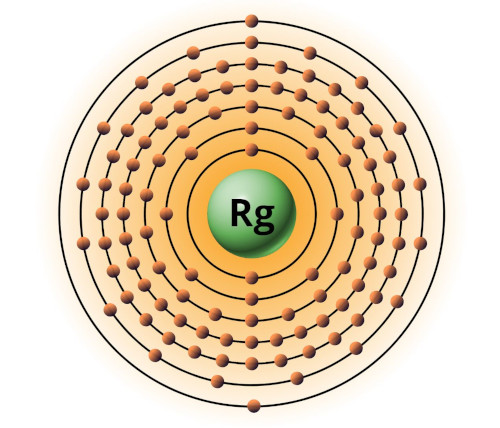 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 2 |
| 112 | Bohr model of Copernicium (Cn) |
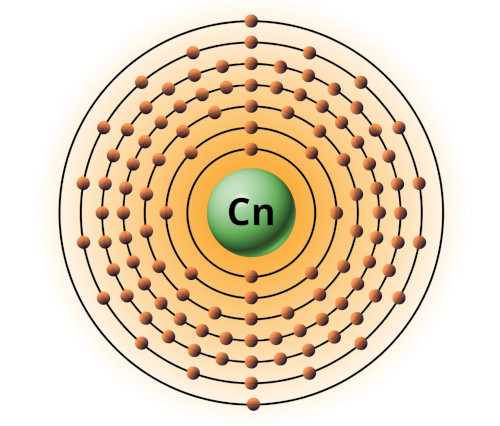 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 2 |
| 113 | Bohr model of Nihonium (Nh) |
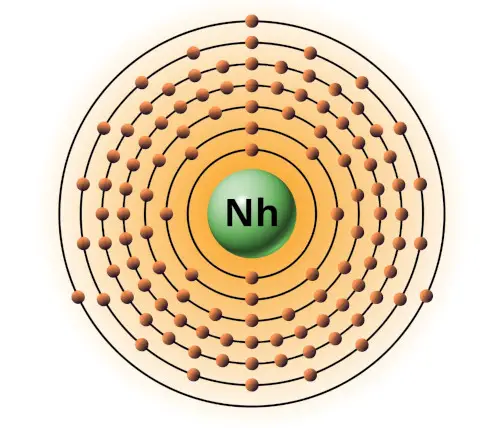 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 3 |
| 114 | Bohr model of Flerovium (Fl) |
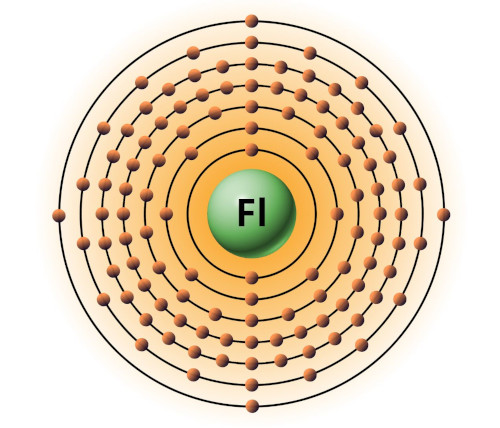 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 4 |
| 115 | Bohr model of Moscovium (Mc) |
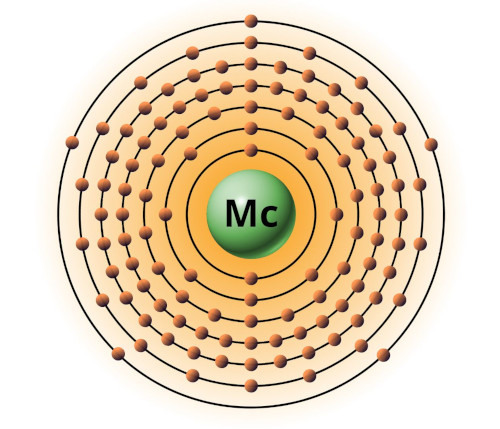 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 5 |
| 116 | Bohr model of Livermorium (Lv) |
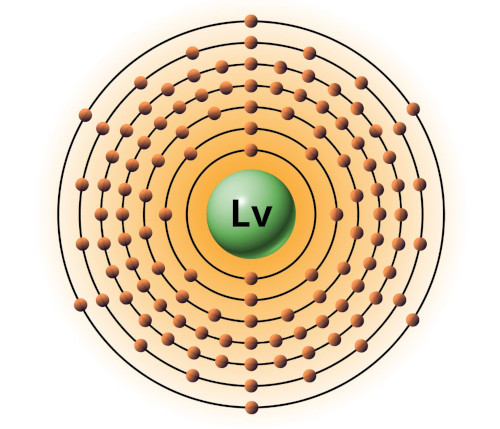 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 6 |
| 117 | Bohr model of Tennessine (Ts) |
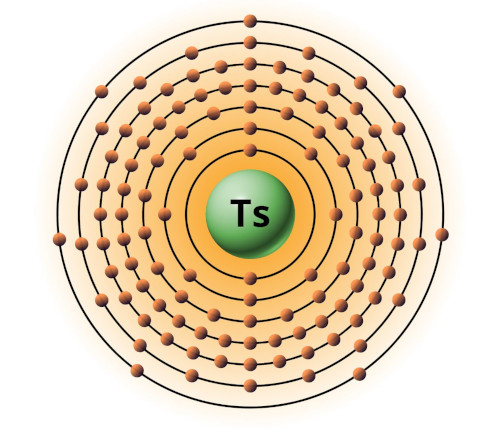 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 7 |
| 118 | Bohr model of Oganesson (Og) |
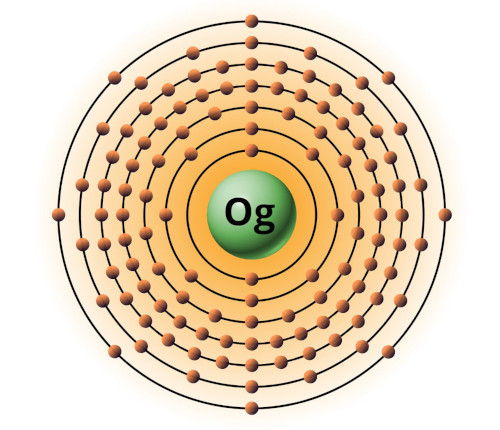 2, 8, 18, 32, 32 18, 8 |
External resources:
- Foundation, C. (n.d.). CK12-Foundation. CK12-Foundation. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-middle-school-physical-science-flexbook-2.0/section/3.15/primary/lesson/bohrs-atomic-model-ms-ps/
- Bohr Diagrams of Atoms and Ions. (2015, September 6). Chemistry LibreTexts. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Electronic_Structure_of_Atoms_and_Molecules/Bohr_Diagrams_of_Atoms_and_Ions
- Bohr model – Wikipedia. (2014, September 30). Bohr Model – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bohr_model
- The Bohr Model of the Atom. (n.d.). The Bohr Model of the Atom | NSTA. https://www.nsta.org/science-teacher/science-teacher-januaryfebruary-2021/bohr-model-atom
- Bohr model. (n.d.). https://cpanhd.sitehost.iu.edu/C101webnotes/modern-atomic-theory/Bohr-model.html
- Bohr model. (n.d.). https://www.pas.rochester.edu/~blackman/ast104/bohr.html
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.