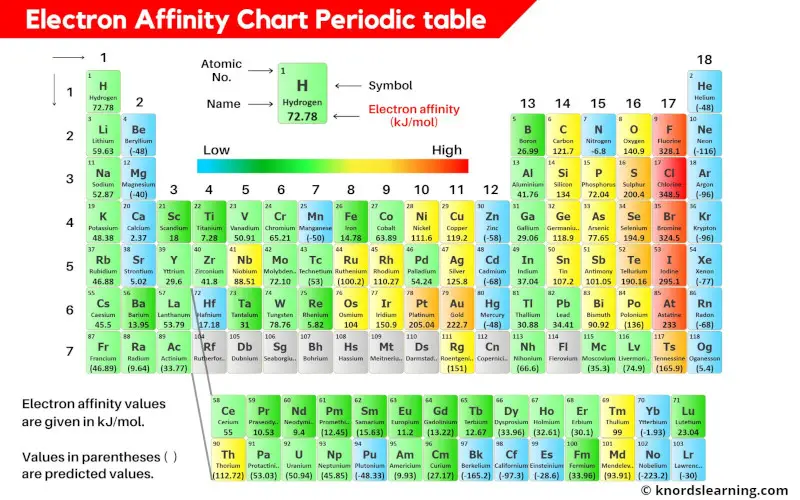
This is a periodic table with electron affinity values mentioned on it.
The values of electron affinity are given in kJ/mol. The values that are written in parentheses ( ) are the predicted values.
You can also see the electron affinity values of all the elements in the table given below.
But before that, you need to understand some important concepts regarding electron affinity.
What is Electron Affinity?
Electron affinity is the amount of energy change (ΔE) that occurs when an electron is added in the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom.
In simple words, when the electron is added to the neutral atom, the energy is either absorbed or released. This amount of energy change (ΔE) is the electron affinity of that atom.
The change in energy (ΔE) can be either positive, negative or zero.
The sign of electron affinity (EEA) is opposite to the sign of energy change (ΔE).
EEA = – (ΔE)
So, if ΔE is positive, then EEA will be negative and if ΔE is negative, then EEA will be positive.
Points to remember:
- For exothermic reaction (i.e when energy is released), the change in energy (ΔE) is negative. Hence the sign of Electron Affinity (EEA) will be positive.
- For endothermic reaction (i.e when energy is absorbed), the change in energy (ΔE) is positive. Hence the sign of Electron Affinity (EEA) will be negative.
- For neutral process (i.e when energy is neither absorbed nor released), the value of Electron Affinity (EEA) will be zero.
More the positive values of Electron Affinity (EEA), more is the energy released.
The halogens (group 17 elements) show more positive values of electron affinity (EEA). This simply indicates that more energy is released in case of halogens when the electron is added to the neutral atom.
Electron Affinity Chart of All Elements of Periodic Table
Electron affinity chart for all the elements of periodic table is shown in the below table.
These values are in kJ/mol and the values written in parentheses ( ) are the predicted values.
| Atomic number | Elements | Electron affinity (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electron affinity of Hydrogen (H) | 72.78 |
| 2 | Electron affinity of Helium (He) | (-48) |
| 3 | Electron affinity of Lithium (Li) | 59.63 |
| 4 | Electron affinity of Beryllium (Be) | (-48) |
| 5 | Electron affinity of Boron (B) | 26.99 |
| 6 | Electron affinity of Carbon (C) | 121.77 |
| 7 | Electron affinity of Nitrogen (N) | -6.8 |
| 8 | Electron affinity of Oxygen (O) | 140.98 |
| 9 | Electron affinity of Fluorine (F) | 328.16 |
| 10 | Electron affinity of Neon (Ne) | (-116) |
| 11 | Electron affinity of Sodium (Na) | 52.87 |
| 12 | Electron affinity of Magnesium (Mg) | (-40) |
| 13 | Electron affinity of Aluminum (Al) | 41.76 |
| 14 | Electron affinity of Silicon (Si) | 134.06 |
| 15 | Electron affinity of Phosphorus (P) | 72.04 |
| 16 | Electron affinity of Sulfur (S) | 200.4 |
| 17 | Electron affinity of Chlorine (Cl) | 348.57 |
| 18 | Electron affinity of Argon (Ar) | (-96) |
| 19 | Electron affinity of Potassium (K) | 48.38 |
| 20 | Electron affinity of Calcium (Ca) | 2.37 |
| 21 | Electron affinity of Scandium (Sc) | 18 |
| 22 | Electron affinity of Titanium (Ti) | 7.28 |
| 23 | Electron affinity of Vanadium (V) | 50.91 |
| 24 | Electron affinity of Chromium (Cr) | 65.21 |
| 25 | Electron affinity of Manganese (Mn) | (-50) |
| 26 | Electron affinity of Iron (Fe) | 14.78 |
| 27 | Electron affinity of Cobalt (Co) | 63.89 |
| 28 | Electron affinity of Nickel (Ni) | 111.65 |
| 29 | Electron affinity of Copper (Cu) | 119.23 |
| 30 | Electron affinity of Zinc (Zn) | (-58) |
| 31 | Electron affinity of Gallium (Ga) | 29.06 |
| 32 | Electron affinity of Germanium (Ge) | 118.93 |
| 33 | Electron affinity of Arsenic (As) | 77.65 |
| 34 | Electron affinity of Selenium (Se) | 194.95 |
| 35 | Electron affinity of Bromine (Br) | 324.53 |
| 36 | Electron affinity of Krypton (Kr) | (-96) |
| 37 | Electron affinity of Rubidium (Rb) | 46.88 |
| 38 | Electron affinity of Strontium (Sr) | 5.02 |
| 39 | Electron affinity of Yttrium (Y) | 29.6 |
| 40 | Electron affinity of Zirconium (Zr) | 41.8 |
| 41 | Electron affinity of Niobium (Nb) | 88.51 |
| 42 | Electron affinity of Molybdenum (Mo) | 72.10 |
| 43 | Electron affinity of Technetium (Tc) | (53) |
| 44 | Electron affinity of Ruthenium (Ru) | (100.27) |
| 45 | Electron affinity of Rhodium (Rh) | 110.27 |
| 46 | Electron affinity of Palladium (Pd) | 54.24 |
| 47 | Electron affinity of Silver (Ag) | 125.86 |
| 48 | Electron affinity of Cadmium (Cd) | (-68) |
| 49 | Electron affinity of Indium (In) | 37.04 |
| 50 | Electron affinity of Tin (Sn) | 107.29 |
| 51 | Electron affinity of Antimony (Sb) | 101.05 |
| 52 | Electron affinity of Tellurium (Te) | 190.16 |
| 53 | Electron affinity of Iodine (I) | 295.15 |
| 54 | Electron affinity of Xenon (Xe) | (-77) |
| 55 | Electron affinity of Caesium (Cs) | 45.5 |
| 56 | Electron affinity of Barium (Ba) | 13.95 |
| 57 | Electron affinity of Lanthanum | 53.79 |
| 58 | Electron affinity of Cerium (Ce) | 55 |
| 59 | Electron affinity of Praseodymium (Pr) | 10.53 |
| 60 | Electron affinity of Neodymium (Nd) | 9.4 |
| 61 | Electron affinity of Promethium (Pm) | (12.45) |
| 62 | Electron affinity of Samarium (Sm) | (15.63) |
| 63 | Electron affinity of Europium (Eu) | 11.2 |
| 64 | Electron affinity of Gadolinium (Gd) | (13.22) |
| 65 | Electron affinity of Terbium (Tb) | 12.67 |
| 66 | Electron affinity of Dysprosium (Dy) | (33.96) |
| 67 | Electron affinity of Holmium (Ho) | (32.61) |
| 68 | Electron affinity of Erbium (Er) | (30.1) |
| 69 | Electron affinity of Thulium (Tm) | 99 |
| 70 | Electron affinity of Ytterbium (Yb) | (-1.93) |
| 71 | Electron affinity of Lutetium (Lu) | 23.04 |
| 72 | Electron affinity of Hafnium (Hf) | 17.18 |
| 73 | Electron affinity of Tantalum (Ta) | 31 |
| 74 | Electron affinity of Tungsten (W) | 78.76 |
| 75 | Electron affinity of Rhenium (Re) | 5.82 |
| 76 | Electron affinity of Osmium (Os) | 104 |
| 77 | Electron affinity of Iridium (Ir) | 150.94 |
| 78 | Electron affinity of Platinum (Pt) | 205.04 |
| 79 | Electron affinity of Gold (Au) | 222.75 |
| 80 | Electron affinity of Mercury (Hg) | (-48) |
| 81 | Electron affinity of Thallium (Tl) | 30.88 |
| 82 | Electron affinity of Lead (Pb) | 34.41 |
| 83 | Electron affinity of Bismuth (Bi) | 90.92 |
| 84 | Electron affinity of Polonium (Po) | (136) |
| 85 | Electron affinity of Astatine (At) | 233 |
| 86 | Electron affinity of Radon (Rn) | (-68) |
| 87 | Electron affinity of Francium (Fr) | (46.89) |
| 88 | Electron affinity of Radium (Ra) | (9.64) |
| 89 | Electron affinity of Actinium (Ac) | (33.77) |
| 90 | Electron affinity of Thorium (Th) | (112.72) |
| 91 | Electron affinity of Protactinium (Pa) | (53.03) |
| 92 | Electron affinity of Uranium (U) | (50.94) |
| 93 | Electron affinity of Neptunium (Np) | (45.85) |
| 94 | Electron affinity of Plutonium (Pu) | (-48.33) |
| 95 | Electron affinity of Americium (Am) | (9.93) |
| 96 | Electron affinity of Curium (Cm) | (27.17) |
| 97 | Electron affinity of Berkelium (Bk) | (-165.24) |
| 98 | Electron affinity of Californium (Cf) | (-97.31) |
| 99 | Electron affinity of Einsteinium (Es) | (-28.6) |
| 100 | Electron affinity of Fermium (Fm) | (33.96) |
| 101 | Electron affinity of Mendelevium (Md) | (93.91) |
| 102 | Electron affinity of Nobelium (No) | (-223.22) |
| 103 | Electron affinity of Lawrencium (Lr) | (-30.04) |
| 104 | Electron affinity of Rutherfordium (Rf) | unknown |
| 105 | Electron affinity of Dubnium (Db) | unknown |
| 106 | Electron affinity of Seaborgium (Sg) | unknown |
| 107 | Electron affinity of Bohrium (Bh) | unknown |
| 108 | Electron affinity of Hassium (Hs) | unknown |
| 109 | Electron affinity of Meitnerium (Mt) | unknown |
| 110 | Electron affinity of Darmstadtium (Ds) | unknown |
| 111 | Electron affinity of Roentgenium (Rg) | (151) |
| 112 | Electron affinity of Copernicium (Cn) | unknown |
| 113 | Electron affinity of Nihonium (Nh) | (66.6) |
| 114 | Electron affinity of Flerovium (Fl) | unknown |
| 115 | Electron affinity of Moscovium (Mc) | (35.3) |
| 116 | Electron affinity of Livermorium (Lv) | (74.9) |
| 117 | Electron affinity of Tennessine (Ts) | (165.9) |
| 118 | Electron affinity of Oganesson (Og) | (5.403) |
External resources:
- Electron affinity | physics. (n.d.). Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/electron-affinity
- Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), T. I. (n.d.). IUPAC – electron affinity (E01977). IUPAC – Electron Affinity (E01977). https://goldbook.iupac.org/terms/view/E01977
- Electron affinity – Wikipedia. (n.d.). Electron Affinity – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_affinity
- Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. (n.d.). Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. https://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch7/ie_ea.html
- Electron affinity (data page) – Wikipedia. (2018, January 15). Electron Affinity (Data Page) – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_affinity_(data_page)
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.