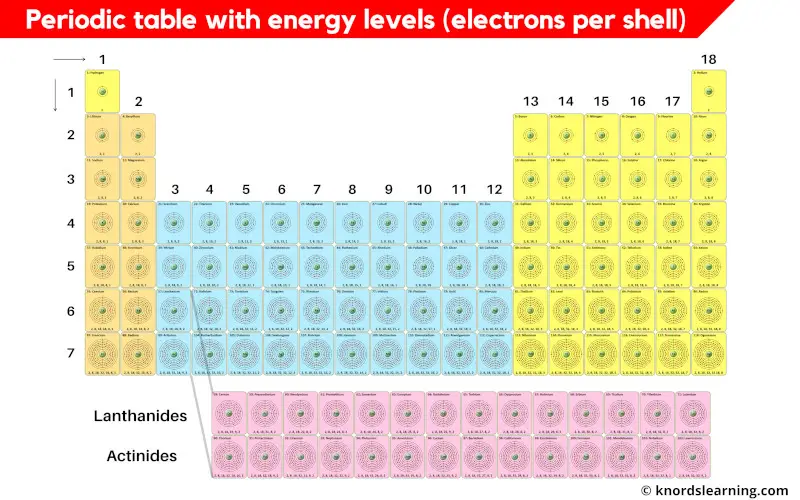
Periodic table with energy levels or electrons per shell is shown in the above image.
I know you are unable to see the shell diagrams in the above periodic table, so here is a HD Image for you.
Also see:
Periodic table with electron configuration labeled on it
Periodic table with atomic mass labeled on it
Periodic table with charges labeled on it
I have also mentioned the electrons per shell (i.e energy levels) of all the elements in the table below.
But before that, you need to know how many electrons can be accommodated in each shell?
Here is a simple table showing the number of electrons that can be accommodated in each shell.
Number of electrons in each shell;
| Orbit / Shell (n) | Maximum no. of electrons this orbit can hold |
|---|---|
| K shell, n = 1 | 2 × 1² = 2 |
| L shell, n = 2 | 2 × 2² = 8 |
| M shell, n = 3 | 2 × 3² = 18 |
| N shell, n = 4 | 2 × 4² = 32 |
| . | . |
| . | . |
| . | . |
Thus, 1st shell can hold 2 electrons, 2nd shell can hold 8 electrons, 3rd shell can hold 18 electrons, 4th shell can hold 32 electrons, and so on.
Now let’s see the energy levels (electrons per shell) of all the elements of periodic table.
Periodic Table Elements and their Electrons Per Shell (or Energy Levels)
| Atomic no. | Element | Electrons per shell (Energy levels) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen (H) | 1 |
| 2 | Helium (He) | 2 |
| 3 | Lithium (Li) | 2, 1 |
| 4 | Beryllium (Be) | 2, 2 |
| 5 | Boron (B) | 2, 3 |
| 6 | Carbon (C) | 2, 4 |
| 7 | Nitrogen (N) | 2, 5 |
| 8 | Oxygen (O) | 2, 6 |
| 9 | Fluorine (F) | 2, 7 |
| 10 | Neon (Ne) | 2, 8 |
| 11 | Sodium (Na) | 2, 8 , 1 |
| 12 | Magnesium (Mg) | 2, 8 , 2 |
| 13 | Aluminum (Al) | 2, 8 , 3 |
| 14 | Silicon (Si) | 2, 8 , 4 |
| 15 | Phosphorus (P) | 2, 8 , 5 |
| 16 | Sulfur (S) | 2, 8 , 6 |
| 17 | Chlorine (Cl) | 2, 8 , 7 |
| 18 | Argon (Ar) | 2, 8 , 8 |
| 19 | Potassium (K) | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| 20 | Calcium (Ca) | 2, 8, 8, 2 |
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) | 2, 8, 9, 2 |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) | 2, 8, 10, 2 |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) | 2, 8, 11, 2 |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) | 2, 8, 13, 1 |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) | 2, 8, 13, 2 |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) | 2, 8, 14, 2 |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) | 2, 8, 15, 2 |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) | 2, 8, 16, 2 |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) | 2, 8, 18, 1 |
| 30 | Zinc (Zn) | 2, 8, 18, 2 |
| 31 | Gallium (Ga) | 2, 8, 18, 3 |
| 32 | Germanium (Ge) | 2, 8, 18, 4 |
| 33 | Arsenic (As) | 2, 8, 18, 5 |
| 34 | Selenium (Se) | 2, 8, 18, 6 |
| 35 | Bromine (Br) | 2, 8, 18, 7 |
| 36 | Krypton (Kr) | 2, 8, 18, 8 |
| 37 | Rubidium (Rb) | 2, 8, 18, 8, 1 |
| 38 | Strontium (Sr) | 2, 8, 18, 8, 2 |
| 39 | Yttrium (Y) | 2, 8, 18, 9, 2 |
| 40 | Zirconium (Zr) | 2, 8, 18, 10, 2 |
| 41 | Niobium (Nb) | 2, 8, 18, 12, 1 |
| 42 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 2, 8, 18, 13, 1 |
| 43 | Technetium (Tc) | 2, 8, 18, 13, 2 |
| 44 | Ruthenium (Ru) | 2, 8, 18, 15, 1 |
| 45 | Rhodium (Rh) | 2, 8, 18, 16, 1 |
| 46 | Palladium (Pd) | 2, 8, 18, 18 |
| 47 | Silver (Ag) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 |
| 48 | Cadmium (Cd) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 |
| 49 | Indium (In) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 3 |
| 50 | Tin (Sn) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 4 |
| 51 | Antimony (Sb) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 5 |
| 52 | Tellurium (Te) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 6 |
| 53 | Iodine (I) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 7 |
| 54 | Xenon (Xe) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 |
| 55 | Caesium (Cs) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1 |
| 56 | Barium (Ba) | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2 |
| 57 | Lanthanum | 2, 8, 18, 18, 9, 2 |
| 58 | Cerium (Ce) | 2, 8, 18, 19, 9, 2 |
| 59 | Praseodymium (Pr) | 2, 8, 18, 21, 8, 2 |
| 60 | Neodymium (Nd) | 2, 8, 18, 22, 8, 2 |
| 61 | Promethium (Pm) | 2, 8, 18, 23, 8, 2 |
| 62 | Samarium (Sm) | 2, 8, 18, 24, 8, 2 |
| 63 | Europium (Eu) | 2, 8, 18, 25, 8, 2 |
| 64 | Gadolinium (Gd) | 2, 8, 18, 25, 9, 2 |
| 65 | Terbium (Tb) | 2, 8, 18, 27, 8, 2 |
| 66 | Dysprosium (Dy) | 2, 8, 18, 28, 8, 2 |
| 67 | Holmium (Ho) | 2, 8, 18, 29, 8, 2 |
| 68 | Erbium (Er) | 2, 8, 18, 30, 8, 2 |
| 69 | Thulium (Tm) | 2, 8, 18, 31, 8, 2 |
| 70 | Ytterbium (Yb) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 8, 2 |
| 71 | Lutetium (Lu) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 9, 2 |
| 72 | Hafnium (Hf) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 10, 2 |
| 73 | Tantalum (Ta) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 11, 2 |
| 74 | Tungsten (W) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 12, 2 |
| 75 | Rhenium (Re) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 13, 2 |
| 76 | Osmium (Os) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2 |
| 77 | Iridium (Ir) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 15, 2 |
| 78 | Platinum (Pt) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 17, 1 |
| 79 | Gold (Au) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 1 |
| 80 | Mercury (Hg) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 2 |
| 81 | Thallium (Tl) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 3 |
| 82 | Lead (Pb) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 4 |
| 83 | Bismuth (Bi) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5 |
| 84 | Polonium (Po) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 6 |
| 85 | Astatine (At) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 7 |
| 86 | Radon (Rn) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8 |
| 87 | Francium (Fr) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 1 |
| 88 | Radium (Ra) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8, 2 |
| 89 | Actinium (Ac) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2 |
| 90 | Thorium (Th) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 10, 2 |
| 91 | Protactinium (Pa) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 20, 9, 2 |
| 92 | Uranium (U) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 21, 9, 2 |
| 93 | Neptunium (Np) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 22, 9, 2 |
| 94 | Plutonium (Pu) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 24, 8, 2 |
| 95 | Americium (Am) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 8, 2 |
| 96 | Curium (Cm) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 25, 9, 2 |
| 97 | Berkelium (Bk) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2 |
| 98 | Californium (Cf) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 28, 8, 2 |
| 99 | Einsteinium (Es) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 29, 8, 2 |
| 100 | Fermium (Fm) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 30, 8, 2 |
| 101 | Mendelevium (Md) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 31, 8, 2 |
| 102 | Nobelium (No) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 2 |
| 103 | Lawrencium (Lr) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 3 |
| 104 | Rutherfordium (Rf) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 10, 2 |
| 105 | Dubnium (Db) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 11, 2 |
| 106 | Seaborgium (Sg) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 12, 2 |
| 107 | Bohrium (Bh) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 13, 2 |
| 108 | Hassium (Hs) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 14, 2 |
| 109 | Meitnerium (Mt) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 15, 2 |
| 110 | Darmstadtium (Ds) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 1 |
| 111 | Roentgenium (Rg) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 2 |
| 112 | Copernicium (Cn) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 2 |
| 113 | Nihonium (Nh) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 3 |
| 114 | Flerovium (Fl) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 4 |
| 115 | Moscovium (Mc) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 5 |
| 116 | Livermorium (Lv) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 6 |
| 117 | Tennessine (Ts) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 7 |
| 118 | Oganesson (Og) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 8 |
External resources:
- Electron shell – Wikipedia. (n.d.). Electron Shell – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_shell
- 2.5: Arrangement of Electron (Shell Model). (2014, July 3). Chemistry LibreTexts. https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Sacramento_City_College/SCC%3A_Chem_309_-_General_Organic_and_Biochemistry_(Bennett)/Text/02._Atomic_Structure/2.5%3A_Arrangement_of_Electron_(Shell_Model)
- Lecture 6: Electron Shell Model, Quantum Numbers, and PES | Introduction to Solid State Chemistry | Materials Science and Engineering | MIT OpenCourseWare. (n.d.). MIT OpenCourseWare. https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/3-091-introduction-to-solid-state-chemistry-fall-2018/resources/lecture-6/
- The energy of an electron. (n.d.). http://www.chem.uiuc.edu/rogers/text5/Tx52/tx52.html
- The periodic table, electron shells, and orbitals (article) | Khan Academy. (n.d.). Khan Academy. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-chemistry-beta/x2eef969c74e0d802:atomic-structure-and-properties/x2eef969c74e0d802:atomic-structure-and-electron-configuration/a/the-periodic-table-electron-shells-and-orbitals-article
- Electron shell | Definition & Facts. (n.d.). Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/electron-shell
- Foundation, C. (n.d.). CK12-Foundation. CK12-Foundation. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-chemistry-flexbook-2.0/section/5.12/primary/lesson/energy-level-ms-ps/
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.