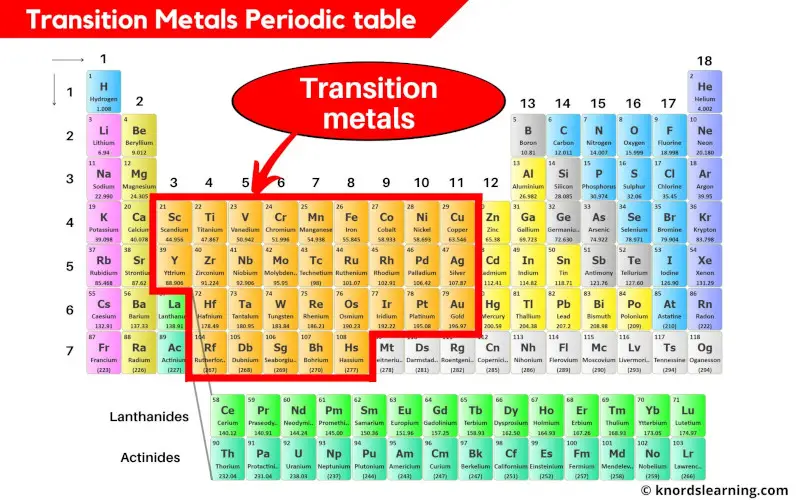
Transition metals are the elements that are lying in the middle of the periodic table from group 3 to group 11. There are a total 31 commonly known transition metals on the periodic table.
But many students have confusion regarding whether group 12 elements are transition metals or not?
Also they have confusion whether lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac) are included as transition metals or not?
I’ve explained everything below.
So let’s dive right into it.
Table of contents
- What are transition metals? Why are they called so?
- Definition of transition metals by IUPAC
- How many transition metals are on the periodic table?
- List of transition metals
What are transition metals? Why are transition metals called so?
The transition metals are the elements whose properties show a transition from electropositive elements of s-block to the electronegative elements of p-block.
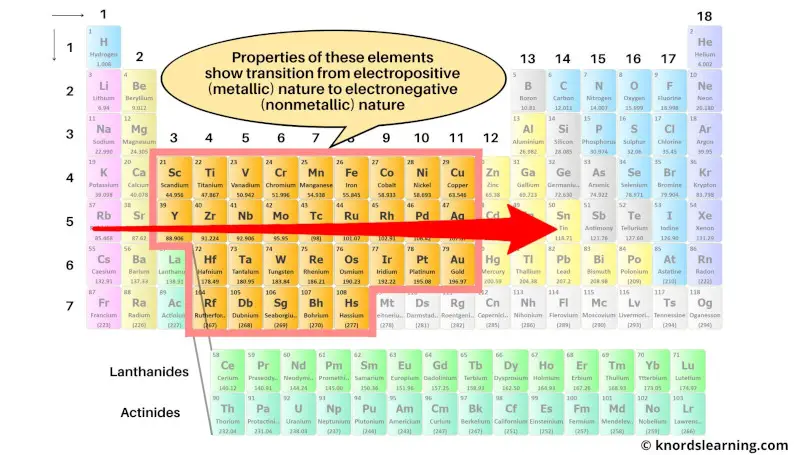
These transition elements form a bridge between the best metals (on the left side) and best nonmetals (on the right side).
As the properties of these elements show transition from electropositive nature to electronegative nature, they are called transition metals.
Now let’s see the definition of transition metals.
Definition of transition elements by IUPAC
Transition elements (or transition metals) are those elements which have partially filled d-orbitals, either in their ground state (M) or most common oxidation states (M1+, M2+, etc).
Let’s understand this definition by using 2 examples.
Example 1: Copper
If we see the ground state of copper, then it is a state when copper has neither lost nor gained electrons. So the ground state of copper is Cu.
Now if we see the most common oxidation state of copper, then it is Cu2+. This is because copper mostly loses 2 electrons during a chemical reaction to become Cu2+ ion.
So,
The electron configuration of Cu is: [Ar] 3d10 4s1 and
The electron configuration of Cu2+ is: [Ar] 3d9
In this most common oxidation state, the copper has partially filled d-orbitals.
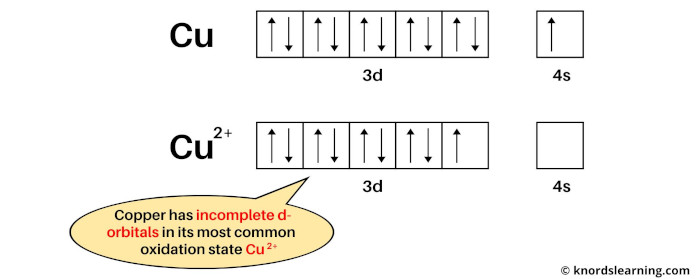
From the above image, you can see that the elemental state (or ground state) of copper has completely filled d-orbitals, but its most common oxidation state (i.e Cu2+) has incompletely filled d-orbitals.
So, according to the definition of transition metals, the copper element is a transition metal.
Example 2: Zinc
If we see the ground state of zinc, then it is a state when zinc has neither lost nor gained electrons. So the ground state of zinc is Zn.
Now if we see the most common oxidation state of zinc, then it is Zn2+. This is because copper mostly loses 2 electrons during a chemical reaction to become Zn2+ ion.
So,
The electron configuration of Zn is: [Ar] 3d10 4s2 and
The electron configuration of Zn2+ is: [Ar] 3d10
According to the definition of transition metals, there must be incomplete d-orbitals either in the ground state or most common oxidation state; then only the element is called a transition metal.
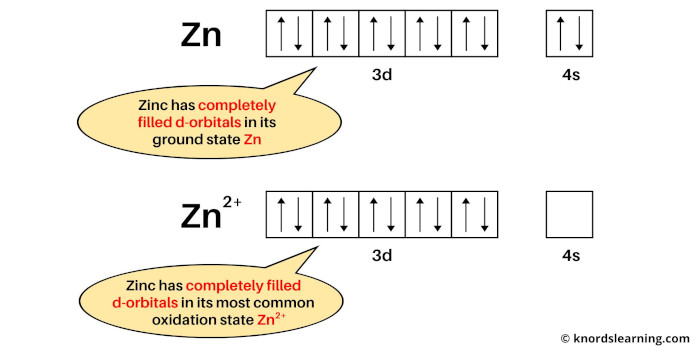
From the above image, you can see that the elemental state (or ground state) of zinc has completely filled d-orbitals, and its most common oxidation state (i.e Zn2+) also has completely filled d-orbitals.
So, according to the definition of transition metals, the zinc element is not a transition metal.
I hope you have clearly understood the definition of transition elements with the above examples.
Now let’s see how many transition metals are there on the periodic table.
How many transition metals are on the periodic table?
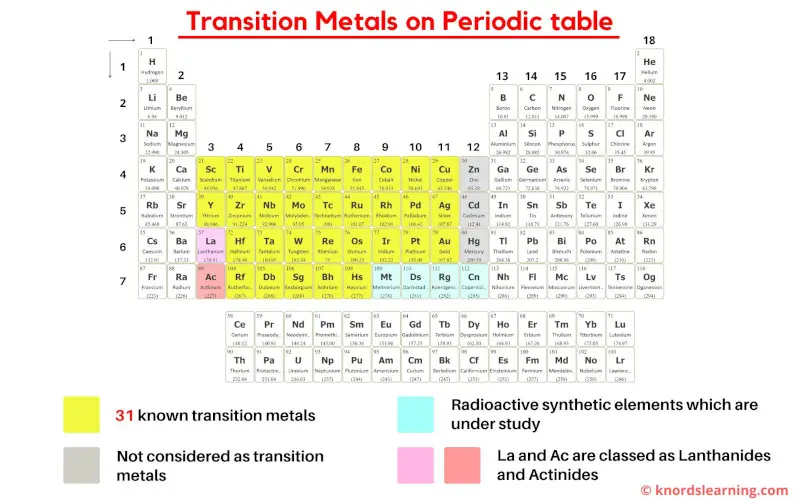
As per the definition of transition metals by IUPAC, there are 31 commonly known transition metals on the periodic table.
But this number is not true as there are various different definitions of transition metals according to different authors.
- According to the definition given by IUPAC, the group 12 elements (Zn, Cd and Hg) are not considered as transition metals because they do not have incomplete d-orbitals either in their elemental state (Zn, Cd, Hg) or oxidation state (Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+).
- Some authors have defined transition elements on the basis of electron configuration, while some gave definitions based on chemical properties, while the definition of transition metals is also somewhat different in inorganic chemistry textbooks.
- Also on the basis of electronic configuration, some researchers have included Lanthanum (La) and Actinium (Ac) as transition metals, but according to Aufbau principle and inorganic chemistry, La and Ac are not considered as transition elements.
So to avoid this confusion, just remember these 3 points for transition metals.
Summary of your confusion
- Finally as a summary, simply remember that the elements lying from group 3 to 11 are the transition metals on the periodic table.
- If La and Ac are included, then there are total of 33 transition metals on the Periodic table.
- And if La and Ac are excluded, then there are total of 31 transition metals on Periodic table.
List of transition metals
List of transition metals is mentioned below.
| Atomic number | Name and symbol of element |
|---|---|
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) |
| 39 | Yttrium (Y) |
| 40 | Zirconium (Zr) |
| 41 | Niobium (Nb) |
| 42 | Molybdenum (Mo) |
| 43 | Technetium (Tc) |
| 44 | Ruthenium (Ru) |
| 45 | Rhodium (Rh) |
| 46 | Palladium (Pd) |
| 47 | Silver (Ag) |
| 57 | Lanthanum (La) [if included] |
| 72 | Hafnium (Hf) |
| 73 | Tantalum (Ta) |
| 74 | Tungsten (W) |
| 75 | Rhenium (Re) |
| 76 | Osmium (Os) |
| 77 | Iridium (Ir) |
| 78 | Platinum (Pt) |
| 79 | Gold (Au) |
| 89 | Actinium (Ac) [if included] |
| 104 | Rutherfordium (Rf) |
| 105 | Dubnium (Db) |
| 106 | Seaborgium (Sb) |
| 107 | Bohrium (Bh) |
| 108 | Hassium (Hs) |
External resources:
- Transition metal – Wikipedia. (2021, January 28). Transition Metal – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transition_metal
- Boudreaux, K. A. (n.d.). The Parts of the Periodic Table. The Parts of the Periodic Table. https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/periodic/trans_transition.htm
- Introduction to Transition Metals II. (2013, October 3). Chemistry LibreTexts. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Inorganic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_and_Websites_(Inorganic_Chemistry)/Descriptive_Chemistry/Elements_Organized_by_Block/3_d-Block_Elements/1b_Properties_of_Transition_Metals/Introduction_to_Transition_Metals_II
- Foundation, C. (n.d.). CK12-Foundation. CK12-Foundation. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-middle-school-physical-science-flexbook-2.0/section/4.9/primary/lesson/transition-metals-ms-ps/
- Transition Metals. (n.d.). Transition Metals. https://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch12/trans.php
- Introducing transition metals. (n.d.). Introducing Transition Metals. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/inorganic/transition/features.html
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.