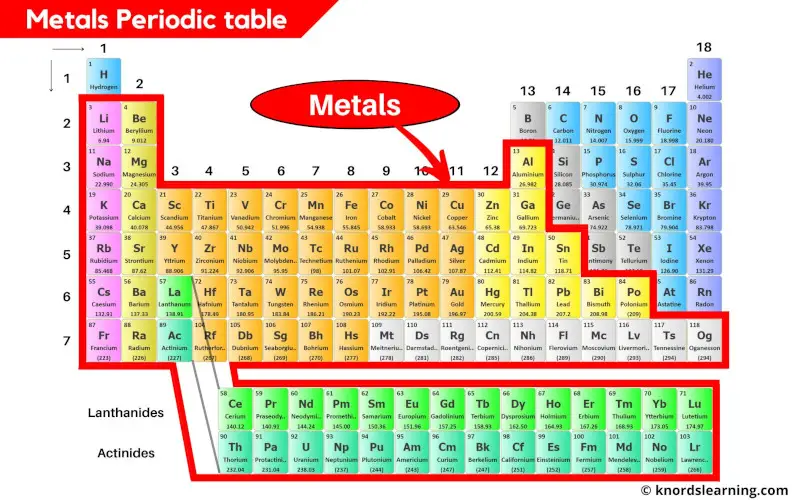
Metals contribute the major part of the periodic table. Almost 78% of the elements present on the periodic table are metals.
You can see that the metals are located on the left side of the periodic table.
Well there are many more things about the metals of periodic table.
So let’s dive right into it.
Table of contents
- What exactly are the metals?
- Alkali metals periodic table
- Alkaline earth metals periodic table
- Transition metals periodic table
- Inner transition metals periodic table
- Post transition metals periodic table
- Rare earth metals periodic table
- Heavy metals periodic table
- Reactive metals periodic table
- List of metals on the periodic table
What exactly are the metals?

Metals are the elements which are usually hard and shiny, and they can conduct heat and electricity through it. [1]
Metals are highly ductile as well as malleable, that means they can be drawn into thin wires and sheets.
During a chemical reaction, metals lose the valence electrons and form a positive ion.
You have already seen a few metals like iron, gold, silver, aluminum, copper, etc.
Now let’s see the different types of metals on the periodic table.
Alkali metals periodic table
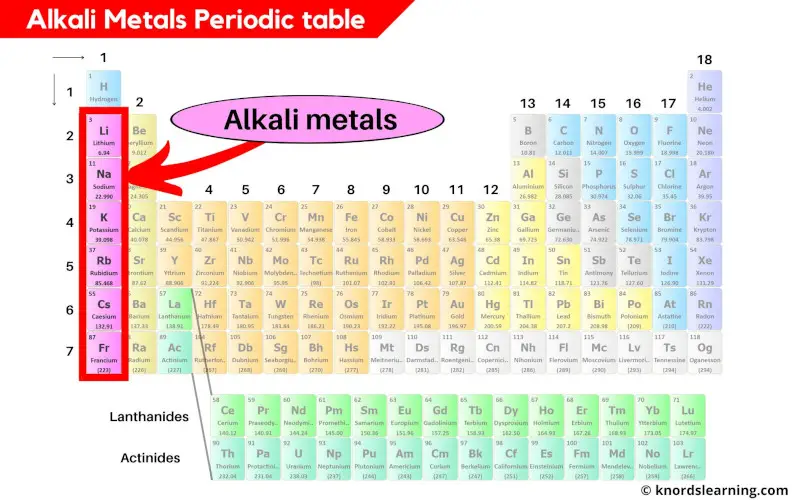
Alkali metals are present in the group 1 of the periodic table.
Alkaline earth metals periodic table
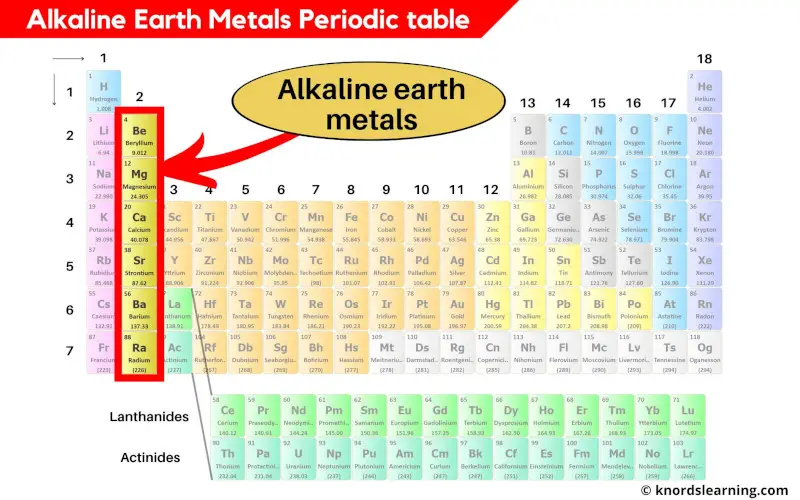
Group 2 elements of the periodic table are known as Alkaline earth metals.
Transition metals periodic table
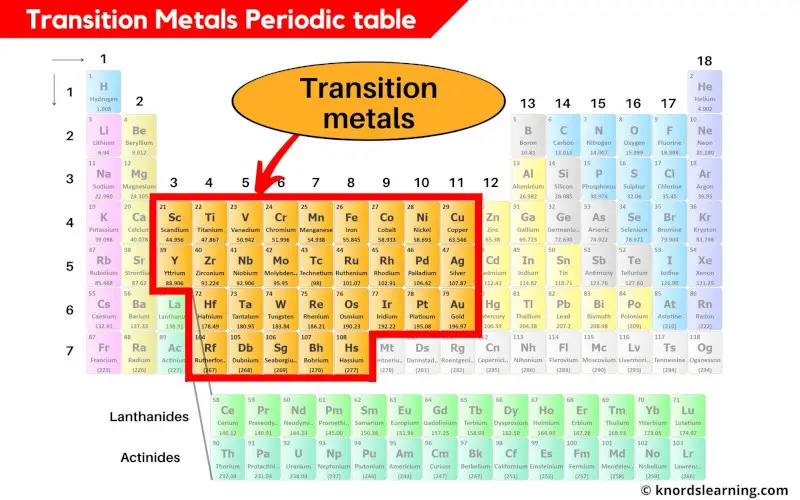
The elements lying from group 3 to group 11 are classified as transition metals.
Inner transition metals periodic table
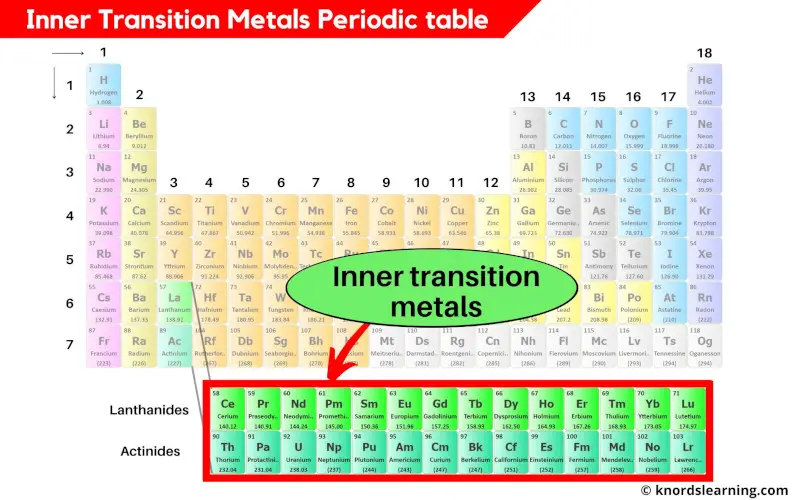
The inner transition metals are placed at the bottom of the periodic table.
The inner transition metals are the part of transition metals only, but they are lying in the inner section of the transition metals. Hence they are known as inner transition metals.
Post transition metals periodic table
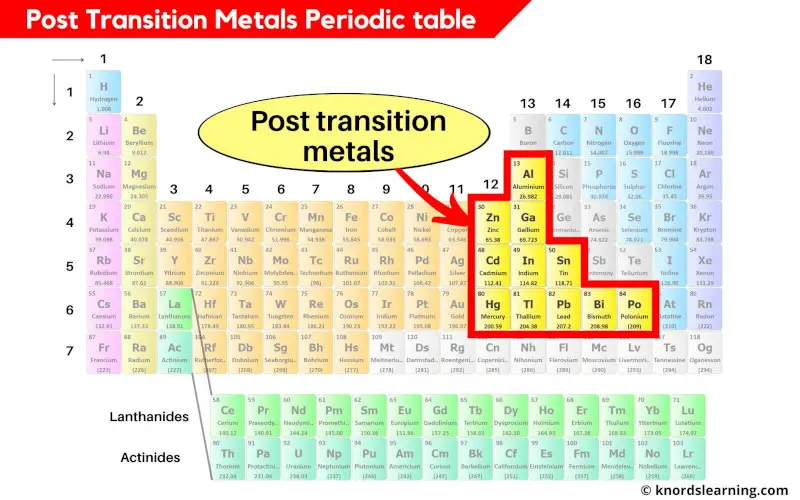
The post transition metals are the metals between the transition metals and metalloids.
Rare earth metals periodic table
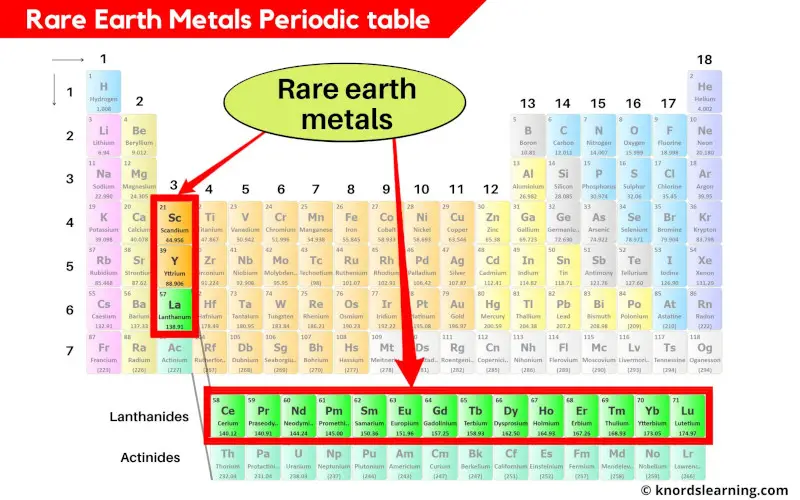
Rare earth metals include all the 15 lanthanides as well as Scandium (Sc) and Yttrium (Y).
Heavy metals periodic table
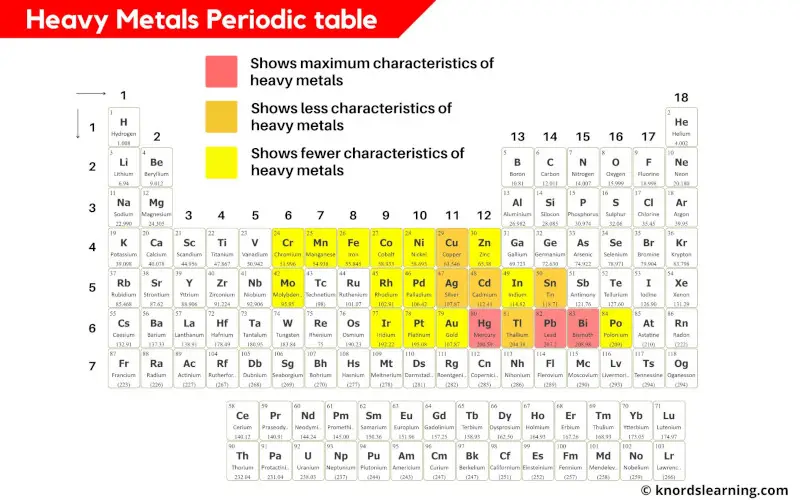
Heavy metals are those metals which have higher densities or higher atomic mass.
Generally the metals having density greater than 5 g/cm3 are considered as heavy metals. [2]
In the above periodic table, you can see the metals that show characteristics of heavy metals.
Reactive metals periodic table

The most reactive metals present on the periodic table are Rubidium (Rb), Cesium (Cs) and Francium (Fr).
Francium (Fr) is available in very less quantity and it is generally made in the laboratory. [3]
So for practical purposes, Cesium (Cs) is considered as a most reactive element on the periodic table.
List of metals on the periodic table
Here is a complete list of all the metals of the periodic table.
| Atomic number | Symbol and Name of element |
|---|---|
| 3 | Li | Lithium |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium |
| 11 | Na | Sodium |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium |
| 13 | Al | Aluminum |
| 19 | K | Potassium |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium |
| 23 | V | Vanadium |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese |
| 26 | Fe | Iron |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel |
| 29 | Cu | Copper |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium |
| 47 | Ag | Silver |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium |
| 49 | In | Indium |
| 50 | Sn | Tin |
| 55 | Cs | Cesium |
| 56 | Ba | Barium |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium |
| 63 | Eu | Europium |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium |
| 68 | Er | Erbium |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum |
| 74 | W | Tungsten |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium |
| 76 | Os | Osmium |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum |
| 79 | Au | Gold |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium |
| 82 | Pb | Lead |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth |
| 84 | Po | Polonium |
| 87 | Fr | Francium |
| 88 | Ra | Radium |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium |
| 90 | Th | Thorium |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium |
| 92 | U | Uranium |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium |
| 95 | Am | Americium |
| 96 | Cm | Curium |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium |
| 98 | Cf | Californium |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium |
| 102 | No | Nobelium |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson |
External resources:
- Information on Alkali Metals – Stanford Environmental Health & Safety. (n.d.). Information on Alkali Metals – Stanford Environmental Health & Safety. http://ehs.stanford.edu/reference/information-alkali-metals
- Metal – Wikipedia. (2021, March 25). Metal – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metal
- Boudreaux, K. A. (n.d.). The Parts of the Periodic Table. The Parts of the Periodic Table. http://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/periodic/physical_metals.htm
- Dye, J. L. (2015, March 13). The alkali metals: 200 years of surprises. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 373(2037), 20140174. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2014.0174
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.