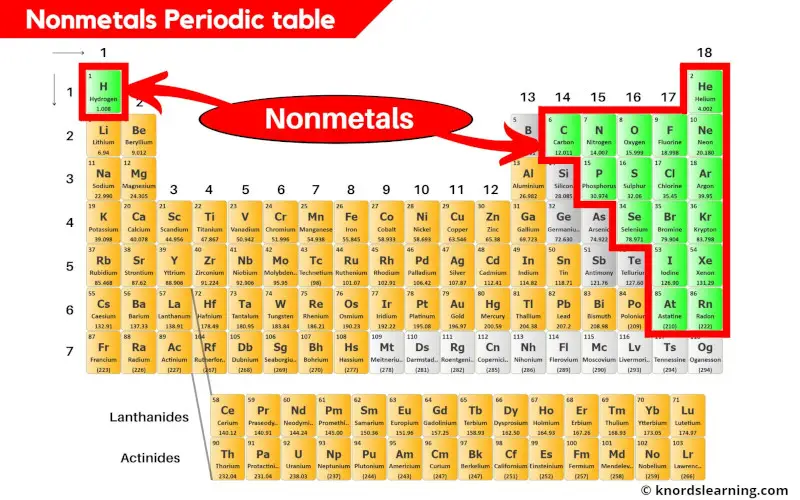
Nonmetals on the periodic table are the elements that do not possess the metallic properties.
There are 18 nonmetals on the periodic table.
These nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table (except hydrogen which is on the left side.)
Well there are a lot more things to know about nonmetals on the periodic table.
So let’s dive right into it.
Table of contents
- What exactly are the Nonmetals?
- How many Nonmetals are on the Periodic table?
- List of nonmetals
- Physical properties of Nonmetals
- Chemical properties of Nonmetals
What exactly are the Nonmetals?
Nonmetals are the elements that are not the metals.
Nonmetals are soft and dull. They don’t show properties like lustrous surface, malleability, ductility as well as they have very poor thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. [1]
Also during the chemical reactions, the nonmetal elements gain electrons and become negative ions.
Few examples of non metals that you already know are;
Oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine, etc.
How many Nonmetals are on the Periodic table?
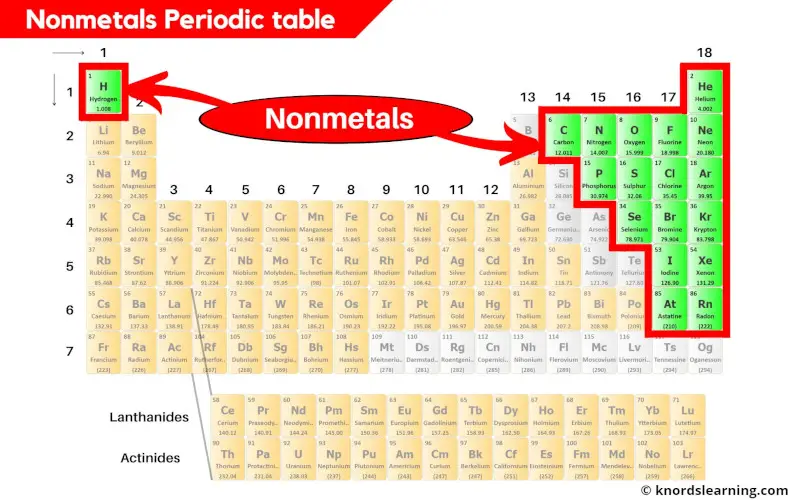
There are a total 18 nonmetals present on the periodic table.
You can see in the above image that the nonmetals are present on the right side of the periodic table. (Hydrogen is the nonmetal that is present on the left top corner of the periodic table.)
The element 85 (i.e Astatine (At)) shows the properties similar to halogens as well as metalloids.
But according to researchers, most of the properties of Astatine (At) are similar to that of halogens (and halogens are nonmetals). [2]
So, the Astatine (At) is classified as a nonmetals on the periodic table.
Hence if Astatine is classified as nonmetal, then there are a total of 18 nonmetals on the periodic table.
And if Astatine is excluded from nonmetals, then there are a total 17 nonmetals.
Reason behind the inexact number of Nonmetals
Actually this number (whether 17 or 18) is inexact because there are different definitions of nonmetals based on chemistry and physics.
Some researchers define nonmetals on the basis of density while some define nonmetals on the basis of chemical properties.
So, as there are no widely accepted definitions of metals, nonmetals and metalloids, the total number of nonmetals present on the periodic table is inexact.
List of Nonmetals
Here is a complete list of all the 18 nonmetals on the periodic table.
| Atomic number | Symbol and Name of element |
|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen |
| 2 | He | Helium |
| 6 | C | Carbon |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen |
| 8 | O | Oxygen |
| 9 | F | Fluorine |
| 10 | Ne | Neon |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus |
| 16 | S | Sulfur |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine |
| 18 | Ar | Argon |
| 34 | Se | Selenium |
| 35 | Br | Bromine |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton |
| 53 | I | Iodine |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon |
| 85 | At | Astatine |
| 86 | Rn | Radon |
Now let’s see some physical properties as well as chemical properties of nonmetals.
Physical properties of Nonmetals
The physical properties of nonmetals are mentioned below.
- Nonmetals exist in solid state, liquid state as well as gaseous state at room temperature. For example, 11 nonmetals exist in gaseous state, Bromine (Br) exist in liquid state, and rest of the nonmetals exist in solid state. [3]
- Nonmetals have very less or no lusture.
- Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- Solid nonmetals are brittle in nature.
- The nonmetals have lower boiling point and melting points.
- Nonmetals have less density and hence they are lightweight.
- Solid nonmetals do not produce sound when they are struck.
Chemical properties of Nonmetals
The chemical properties of nonmetals are mentioned below.
- The number of valence electrons of nonmetals ranges from 4 to 8. Nonmetals of group 14 have 4 valence electrons, nonmetals of group 15 have 5 valence electrons, nonmetals of group 16 have 6 valence electrons, nonmetals of group 17 have 7 valence electrons and nonmetals of group 18 have 8 valence electrons.
- Nonmetals have higher electronegativity, that means they can easily gain electron/s during a chemical reaction.
- The nonmetals form acidic oxides when they react with water.
- Nonmetals are very good oxidizing agents as they get reduced by gaining electron/s during a chemical reaction.
External resources:
- Nonmetal – Wikipedia. (2022, August 27). Nonmetal – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nonmetal
- Yao, B., Kuznetsov, V. L., Xiao, T., Slocombe, D. R., Rao, C. N. R., Hensel, F., & Edwards, P. P. (2020, August 17). Metals and non-metals in the periodic table. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 378(2180), 20200213. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2020.0213
- Foundation, C. (n.d.). CK12-Foundation. CK12-Foundation. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-middle-school-physical-science-flexbook-2.0/section/4.4/primary/lesson/nonmetals-ms-ps
- Boudreaux, K. A. (n.d.). The Parts of the Periodic Table. The Parts of the Periodic Table. https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/periodic/physical_metals.htm
- Properties of metal and non-metal elements – Metals and non-metals – Eduqas – GCSE Chemistry (Single Science) Revision – Eduqas – BBC Bitesize. (n.d.). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zcxmfcw/revision/1
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.