Arsenic element (As) is in group 15 and period 4 of a periodic table. Arsenic is in the p-block and it is classified as a metalloid on the periodic table.
There is a lot more information related to arsenic which is mentioned in the Information Table given below.
So let’s dive right into it!
Table of contents
- Arsenic element (Information Table)
- Arsenic element in Periodic table
- Facts about Arsenic
- Properties of Arsenic
- Uses of Arsenic
Arsenic Element (Information Table)
The important data related to arsenic element is given in the table below.
| Appearance of arsenic | Gray metallic surface |
| Atomic number of arsenic | 33 |
| Symbol of arsenic | As |
| Atomic mass of arsenic | 74.922 u |
| Protons, Neutrons & Electrons in arsenic | Protons: 33, Neutrons: 42, Electrons: 33 |
| State of arsenic (at STP) | Solid |
| Group number of arsenic in periodic table | 15 |
| Period number of arsenic in periodic table | 4 |
| Block of arsenic in periodic table | p-block |
| Category of arsenic | Metalloids |
| Bohr model or Electrons per shell or Electrons arrangement in arsenic | 2, 8, 18, 5 |
| Electron configuration of arsenic | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 |
| Orbital diagram of arsenic | 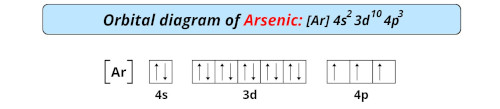 |
| Valence electrons in arsenic | 5 |
| Electronegativity of arsenic (on pauling scale) | 2.18 |
| Atomic radius of arsenic (van der Waals radius) | 185 picometers |
| Density of arsenic | 5.73 g/cm3 |
| 1st ionization energy of arsenic | 9.815 eV |
| Main isotope of arsenic | 75As |
| Sublimation point of arsenic | 887 K or 615 °C or 1137 °F |
| Crystal structure of arsenic | Rhombohedral |
Also see: Interactive Periodic Table (It has rotating bohr models as well as many other details of all the 118 elements in a single periodic table).
Arsenic element in Periodic table
The Arsenic element (As) has the atomic number 33 and is located in group 15 and period 4. Arsenic is a metalloid and it is classified as a pnictogen element.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
Click on above elements in the periodic table to see their information.
Facts about arsenic
Here are a few interesting facts about arsenic element.
- The arsenic element was given its name from the Persian word “Zarnikh” which means “Yellow orpiment”.
- Arsenic is the 53rd most abundant element found from the earth’s crust.
- The arsenic is present in the concentration of 1.8 ppm in the earth’s crust.
- Arsenic causes damage to skin, nervous system, immune system, excretory system, etc.
- Pure arsenic is toxic in nature and it was used as poison.
- Arsenic is mostly found from the igneous rocks on the earth.
Properties of arsenic
Here is a list of some physical properties and chemical properties of arsenic.
Physical properties of arsenic
- At the standard atmospheric pressure, the arsenic transforms directly from solid to gas, which is known as sublimation. And this sublimation temperature is 615 °C.
- Arsenic does not exist in liquid state at standard atmospheric pressure, but it can come to its liquid state at high pressures.
- The density of arsenic is 5.73 g/cm3 and it has an atomic mass of 74.922 u.
- Arsenic has many isotopes including natural as well as radioactive isotopes. Out of these isotopes, the most stable isotope is 75As.
Chemical properties of arsenic
- Arsenic is a metalloid and hence it shows the properties of metals as well as nonmetals.
- The electron configuration of arsenic is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3, and it has the last electron in p-orbitals. So it is a p-block element.
- If the compounds of arsenic are structured with a hammer, then they release characteristic odor.
- Arsenic gets oxidized when heated in the presence of air. During this reaction, the odor is released which is similar to that of garlic.
Uses of arsenic
Here are some uses of the arsenic element.
- Arsenic is used as an alloying metal with other metals to get harder and durable alloy.
- Grey arsenic is a good conductor of electricity, so it is used in industries.
- Arsenic is also used in preventing the wood degradation that occurs due to termites and fungus.
- Arsenic is also used in transistors as a doping agent.
- Gallium arsenide is used in lasers. When the electric current is passed through gallium arsenide, it produces a light.
- Arsenic is used in the manufacturing of insecticides.
External resources:
- Arsenic – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Arsenic – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/33/arsenic
- P. (n.d.). Arsenic | As (Element) – PubChem. Arsenic | as (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Arsenic
- Arsenic – Wikipedia. (2018, February 25). Arsenic – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsenic
- The Facts on Arsenic | Dartmouth Toxic Metals. (n.d.). The Facts on Arsenic | Dartmouth Toxic Metals. https://sites.dartmouth.edu/toxmetal/arsenic/the-facts-on-arsenic/
- What is Arsenic? – Arsenic – University of Maine. (n.d.). What Is Arsenic? – Arsenic – University of Maine. https://umaine.edu/arsenic/what-is-arsenic/
- It’s Elemental – The Element Arsenic. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Arsenic. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele033.html
- Arsenic Statistics and Information | U.S. Geological Survey. (n.d.). Arsenic Statistics and Information | U.S. Geological Survey. https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center/arsenic-statistics-and-information
- Possolo, et al. (2018, January 4). Interpreting and propagating the uncertainty of the standard atomic weights (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 90(2), 395–424. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2016-0402
- Emsley, J. (2011). Nature’s Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. United Kingdom: OUP Oxford.
- Haynes, W. M. (Ed.). (2014, June 4). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. https://doi.org/10.1201/b17118
- Electronic structure of the elements. (2000, March). The European Physical Journal C, 15(1–4), 78–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02683401
- James A. M. & Lord M. P. (1992). Macmillan’s chemical and physical data. Macmillan.
- Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. (n.d.). Periodic Table of Elements: Los Alamos National Laboratory. https://periodic.lanl.gov/33.shtml
- Atomic Data for Arsenic (As). (n.d.). Atomic Data for Arsenic (As). https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Handbook/Tables/arsenictable1.htm
- Arsenic | As | ChemSpider. (n.d.). Arsenic | as | ChemSpider. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.4514330.html?rid=343ecff8-3fb9-44e2-a225-45bc1e16606b
- Bedford, et al. (1996, April 1). Recommended values of temperature on the International Temperature Scale of 1990 for a selected set of secondary reference points. Metrologia, 33(2), 133–154. https://doi.org/10.1088/0026-1394/33/2/3
- Allred, A. (1961, June). Electronegativity values from thermochemical data. Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry, 17(3–4), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1902(61)80142-5
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.