Roentgenium element (Rg) is in group 11 and period 7 of a periodic table. Roentgenium is in the d-block and it is classified as a radioactive synthetic element on the periodic table.
There is a lot more information related to roentgenium which is mentioned in the Information Table given below.
So let’s dive right into it!
Table of contents
- Roentgenium element (Information Table)
- Roentgenium element in Periodic table
- Facts about Roentgenium
- Properties of Roentgenium
- Uses of Roentgenium
Roentgenium Element (Information Table)
The important data related to roentgenium element is given in the table below.
| Appearance of roentgenium | Silvery (predicted) |
| Atomic number of roentgenium | 111 |
| Symbol of roentgenium | Rg |
| Atomic mass of roentgenium (most stable isotope) | 282 u |
| Protons, Neutrons & Electrons in roentgenium | Protons: 111, Neutrons: 161, Electrons: 111 |
| State of roentgenium (at STP) | Solid (predicted) |
| Group number of roentgenium in periodic table | 11 |
| Period number of roentgenium in periodic table | 7 |
| Block of roentgenium in periodic table | d-block |
| Category of roentgenium | Synthetic element |
| Bohr model or Electrons per shell or Electrons arrangement in roentgenium | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 17, 2 |
| Electron configuration of roentgenium | [Rn] 5f14 6d9 7s2 |
| Orbital diagram of roentgenium | 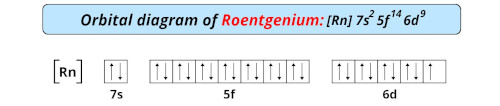 |
| Density of roentgenium (predicted) | 22-24 g/cm3 |
| Crystal structure of roentgenium (predicted) | Body Centered Cubic (BCC) |
Also see: Interactive Periodic Table (It has rotating bohr models as well as many other details of all the 118 elements in a single periodic table).
Roentgenium element in Periodic table
The Roentgenium element (Rg) has the atomic number 111 and is located in group 11 and period 7.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Cs | Ba | La* | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Fr | Ra | Ac** | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
| *Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| **Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
Click on above elements in the periodic table to see their information.
Facts about roentgenium
Here are a few interesting facts about the roentgenium element.
- Roentgenium was given its name to honor the physicist Wilhelm Rontgen.
- Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg discovered the roentgenium element in the year 1994.
- Roentgenium is not available naturally but it is artificially made in the laboratory.
- Roentgenium has around 9 isotopes and all these isotopes are radioactive in nature.
- 282Rg is the most stable isotope of roentgenium which has a half life of only 100 seconds.
Properties of roentgenium
Here is a list of some physical properties and chemical properties of roentgenium.
- Roentgenium is a highly radioactive element and has a very short half life.
- The density of roentgenium is predicted between 22-24 g/cm3 and its most stable isotope has an atomic mass 282 amu.
- Roentgenium is expected to have solid state at room temperature and pressure.
- The crystal structure of roentgenium is BCC (predicted).
- Roentgenium has many oxidation states, but the most stable oxidation state is +3.
Uses of roentgenium
Roentgenium is highly radioactive and it is also very rarely available. So it is not used commercially. It is generally used for research work.
External resources:
- Roentgenium – Wikipedia. (2013, October 4). Roentgenium – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roentgenium
- Roentgenium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table. (n.d.). Roentgenium – Element Information, Properties and Uses | Periodic Table. https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/111/roentgenium
- P. (n.d.). Roentgenium | Rg (Element) – PubChem. Roentgenium | Rg (Element) – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Roentgenium
- It’s Elemental – The Element Roentgenium. (n.d.). It’s Elemental – the Element Roentgenium. https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele111.html
- Sansonetti, J. E., & Martin, W. C. (2005, December). Handbook of Basic Atomic Spectroscopic Data. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 34(4), 1559–2259. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1800011
- Bondi, A. (1964, March). van der Waals Volumes and Radii. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 68(3), 441–451. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100785a001
- Holden, et al. (2018, December 1). IUPAC Periodic Table of the Elements and Isotopes (IPTEI) for the Education Community (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 90(12), 1833–2092. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2015-0703
- Zhang, et al. (2011, January 11). Corrected Values for Boiling Points and Enthalpies of Vaporization of Elements in Handbooks. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 56(2), 328–337. https://doi.org/10.1021/je1011086
- Bedford, et al. (1996, April 1). Recommended values of temperature on the International Temperature Scale of 1990 for a selected set of secondary reference points. Metrologia, 33(2), 133–154. https://doi.org/10.1088/0026-1394/33/2/3
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. With a desire to make learning accessible for everyone, he founded Knords Learning, an online learning platform that provides students with easily understandable explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.